Mucus Relief D | Guaifenesin, Pseudoephedrine Hcl Tablet while Breastfeeding
What is Mucus Relief D | Guaifenesin, Pseudoephedrine Hcl Tablet used for?
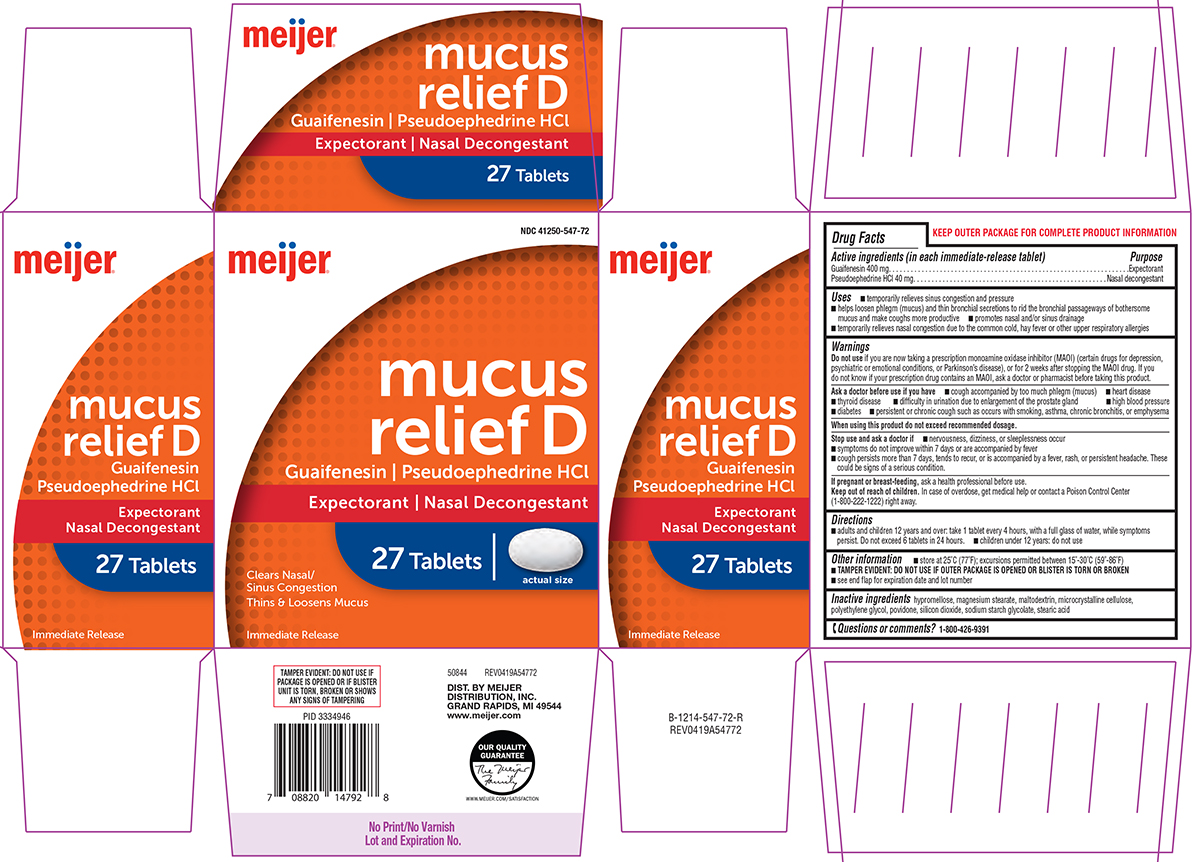
Brief: Expectorant Nasal decongestant
Is Mucus Relief D | Guaifenesin, Pseudoephedrine Hcl Tablet safe to use while breastfeeding? Can it interfere with growth and development of my kid?

Mucus Relief D | Guaifenesin, Pseudoephedrine Hcl Tablet Breastfeeding Analsys
Guaifenesin while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 93-14-1
It is used as an expectorant, alone or in association with other products. Proofs on its effectiveness are sparse. In some instances, preparations of Guaifenesin may contain alcohol as excipient with a concentration as high as 5%. At latest update, relevant published data on excretion into breast milk were not found. Until more information on this medication is available, other option known to be safer would be recommended, mostly in the post-natal period or in cases of prematurity. If used while breastfeeding, a moderate use with the lowest dose as possible and avoiding those preparations with alcoholic excipient, should be preferred. Because effectiveness is poor and likelihood of side effects does exist, especially in multi-association, the US Agency for Drug Administration (FDA) is currently doing efforts for discontinuation of this and others at-the-counter products, that are formulated for cough relief (Guaifenesin, Dextromethorphan, Phenylephrine, Pseudoephedrine, Brompheniramine, etc.)
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 90-82-4
Marketed on multiple compounds as a constituent of antitussives, mucolytics, expectorants and nasal decongestants (Nice 2000).Simple formulations (one active ingredient per drug) are preferable even more while breastfeeding. It is excreted into breast milk in a clinically non-significant amount (Findlay 1984, Kanfer 1993, Nice 2000, Aljazaf 2003) without major problems having been reported in infants whose mothers had received this medication (Ito 1993, Aljazaf 2003, Soasan 2014). Two infants out of ten appeared with mild irritability that did not require medical care (Ito 1993) with only 4 cases related to maternal pseudoephedrine intake having been declared to the French Pharmaceutical Surveillance Database in 26 years (Soasan 2014) . According to one author, it may decrease the milk production, hence a high intake of fluids is recommended to the mother (Nice 2000). Pseudoephedrine produced a variable and non-significant decrease on prolactin levels along with a variable decrease (between 3% and 59%, on average 25%, and a median 15%) on milk production in 8 women whose infants were beyond neonatal period (Aljazaf 2003).Based on the latter single work (Aljazaf 2003), it has been speculated with the use of pseudoephedrine to treat hypergalactia, galactorrhea and to inhibit milk production (Eglash 2014, Trimeloni 2016). Nor-pseudoephedrine was found in the urine of infants whose mothers had consumed a stimulant plant called Catha edulis o cat (Kristiansson 1987). Although not recommended during lactation by some authors (Rubin 1986, Amir 2011), others think it is compatible (Findlay 1984, Ghaeli 1993, Ito 1993, Mitchell 1999, Nice 2000). The American Academy of Pediatrics considers it to be a medication usually compatible with breastfeeding (AAP 2001). It is suggested the use of a lowest effective dose as possible avoiding a long-term use. Monitor milk production, especially if associated with use of Triprolidine (see specific info) during the neonatal period.
Mucus Relief D | Guaifenesin, Pseudoephedrine Hcl Tablet Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Guaifenesin while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 93-14-1
Neither the excretion of guaifenesin in milk nor its effect on breastfed infants have been studied. It is unlikely that with usual maternal doses amounts in breastmilk would harm the nursing infant, especially in infants over 2 months of age. It is best to avoid the use of products with a high alcohol content while nursing.
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 90-82-4
Although the small amounts of pseudoephedrine in breastmilk are unlikely to harm the nursing infant, it may cause irritability occasionally. A single dose of pseudoephedrine decreases milk production acutely and repeated use seems to interfere with lactation. Mothers with newborns whose lactation is not yet well established or in mothers who are having difficulties producing sufficient milk should not receive pseudoephedrine. A treatment scheme has been reported for mothers with hypergalactia that uses pseudoephedrine to decrease milk supply.[1]
I am nursing mother and I have already used Mucus Relief D | Guaifenesin, Pseudoephedrine Hcl Tablet, what should I do?
During whole lactation period you shall first discuss with your doctor and then together you shall decide whether you shall take that drug or not however if you have already taken Mucus Relief D | Guaifenesin, Pseudoephedrine Hcl Tablet then you shall inform your doctor, But you should not be worried too much as Mucus Relief D | Guaifenesin, Pseudoephedrine Hcl Tablet comes in category of low risk drug.
My health care provider has asked me to use Mucus Relief D | Guaifenesin, Pseudoephedrine Hcl Tablet, what to do?
Mucus Relief D | Guaifenesin, Pseudoephedrine Hcl Tablet comes in category of low risk and if your doctor is aware that you are breastfeeding it should be ok to use
If I am using Mucus Relief D | Guaifenesin, Pseudoephedrine Hcl Tablet, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Not much
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Mucus Relief D | Guaifenesin, Pseudoephedrine Hcl Tablet in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
