Modern medicine has evolved so much so that sooner or later every breastfeeding mother needs to take it in one form or other. Medication that is present in mothers blood will transfer into her breast milk to some extent. Most drugs do so at low levels and pose no real risk to infants but then there are some exceptions. In This post will discuss whether Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet is safe in breast-feeding or not.
What is Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet used for?
CIPRO is a fluoroquinolone antibacterial indicated in adults (18 years of age and older) with the following infections caused by designated, susceptible bacteria and in pediatric patients where indicated: •Skin and Skin Structure Infections (1.1) •Bone and Joint Infections (1.2) •Complicated Intra-Abdominal Infections (1.3) •Infectious Diarrhea (1.4) •Typhoid Fever (Enteric Fever) (1.5) •Uncomplicated Cervical and Urethral Gonorrhea (1.6) •Inhalational Anthrax post-exposure in adult and pediatric patients (1.7) •Plague in adult and pediatric patients (1.8) •Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis (1.9) •Lower Respiratory Tract Infections (1.10) •Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis •Urinary Tract Infections (1.11) •Urinary Tract Infections (UTI) •Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis •Complicated UTI and Pyelonephritis in Pediatric Patients •Acute Sinusitis (1.12) Usage To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of CIPRO and other antibacterial drugs, CIPRO should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (1.13) 1.1 Skin and Skin Structure Infections CIPRO is indicated in adult patients for treatment of skin and skin structure infectionscaused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia stuartii, Morganella morganii, Citrobacter freundii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus epidermidis, or Streptococcus pyogenes. 1.2 Bone and Joint Infections CIPRO is indicated in adult patients for treatment of bone and joint infections caused by Enterobacter cloacae, Serratia marcescens, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 1.3 Complicated Intra-Abdominal Infections CIPRO is indicated in adult patients for treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections (used in combination with metronidazole) caused by Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, or Bacteroides fragilis. 1.4 Infectious Diarrhea CIPRO is indicated in adult patients for treatment of infectious diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli (enterotoxigenic isolates), Campylobacter jejuni, Shigella boydii †, Shigella dysenteriae, Shigella flexneri or Shigella sonnei † when antibacterial therapy is indicated. † Although treatment of infections due to this organism in this organ system demonstrated a clinically significant outcome, efficacy was studied in fewer than 10 patients. 1.5 Typhoid Fever (Enteric Fever) CIPRO is indicated in adult patients for treatment of typhoid fever (enteric fever) caused by Salmonella typhi. The efficacy of ciprofloxacin in the eradication of the chronic typhoid carrier state has not been demonstrated. 1.6 Uncomplicated Cervical and Urethral Gonorrhea CIPRO is indicated in adult patients for treatment of uncomplicated cervical and urethral gonorrhea due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.17 )]. 1.7 Inhalational Anthrax (Post-Exposure) CIPRO is indicated in adults and pediatric patients from birth to 17 years of age for inhalational anthrax (post-exposure) to reduce the incidence or progression of disease following exposure to aerosolized Bacillus anthracis. Ciprofloxacin serum concentrations achieved in humans served as a surrogate endpoint reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit and provided the initial basis for approval of this indication.1 Supportive clinical information for ciprofloxacin for anthrax post-exposure prophylaxis was obtained during the anthrax bioterror attacks of October 2001 [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. 1.8 Plague CIPRO is indicated for treatment of plague, including pneumonic and septicemic plague, due to Yersinia pestis (Y. pestis) and prophylaxis for plague in adults and pediatric patients from birth to 17 years of age. Efficacy studies of ciprofloxacin could not be conducted in humans with plague for feasibility reasons. Therefore this indication is based on an efficacy study conducted in animals only [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. 1.9 Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis CIPRO is indicated in adult patients for treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis caused by Escherichia coli or Proteus mirabilis. 1.10 Lower Respiratory Tract Infections CIPRO is indicated in adult patients for treatment of lower respiratory tract infections caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, or Streptococcus pneumoniae. CIPRO is not a drug of first choice in the treatment of presumed or confirmed pneumonia secondary to Streptococcus pneumoniae. CIPRO is indicated for the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis (AECB) caused by Moraxella catarrhalis. Because fluoroquinolones, including CIPRO, have been associated with serious adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1–5.16 )] and for some patients AECB is self-limiting, reserve CIPRO for treatment of AECB in patients who have no alternative treatment options. 1.11 Urinary Tract Infections Urinary Tract Infections in Adults CIPRO is indicated in adult patients for treatment of urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Serratia marcescens, Proteus mirabilis, Providencia rettgeri, Morganella morganii, Citrobacter koseri, Citrobacter freundii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, or Enterococcus faecalis. Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis CIPRO is indicated in adult female patients for treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis caused by Escherichia coli or Staphylococcus saprophyticus. Because fluoroquinolones, including CIPRO, have been associated with serious adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1-5.16)] and for some patients acute uncomplicated cystitis is self-limiting, reserve CIPRO for treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis in patients who have no alternative treatment options. Complicated Urinary Tract Infection and Pyelonephritis in Pediatric Patients CIPRO is indicated in pediatric patients aged one to 17 years of age for treatment of complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI) and pyelonephritis due to Escherichia coli [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. Although effective in clinical trials, CIPRO is not a drug of first choice in the pediatric population due to an increased incidence of adverse reactions compared to controls, including reactions related to joints and/or surrounding tissues. CIPRO, like other fluoroquinolones, is associated with arthropathy and histopathological changes in weight-bearing joints of juvenile animals [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.13 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)]. 1.12 Acute Sinusitis CIPRO is indicated in adult patients for treatment of acute sinusitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, or Moraxella catarrhalis. Because fluoroquinolones, including CIPRO, have been associated with serious adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1-5.15)] and for some patients acute sinusitis is self-limiting, reserve CIPRO for treatment of acute sinusitis in patients who have no alternative treatment options. 1.13 Usage To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of CIPRO and other antibacterial drugs, CIPRO should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy. If anaerobic organisms are suspected of contributing to the infection, appropriate therapy should be administered. Appropriate culture and susceptibility tests should be performed before treatment in order to isolate and identify organisms causing infection and to determine their susceptibility to ciprofloxacin. Therapy with CIPRO may be initiated before results of these tests are known; once results become available appropriate therapy should be continued. As with other drugs, some isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa may develop resistance fairly rapidly during treatment with ciprofloxacin. Culture and susceptibility testing performed periodically during therapy will provide information not only on the therapeutic effect of the antimicrobial agent but also on the possible emergence of bacterial resistance.
Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet while breastfeeding safe or not? Can there be any side effects for infant while using it during breastfeeding?
As per our analysis Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet contains only one ingredient and that is Ciprofloxacin. We have analyzed Ciprofloxacin and it seems to be safe to use Ciprofloxacin while breastfeeding, that means usage of Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet shall be safe while breastfeeding. Below you can check more details of Ciprofloxacin usage in breastfeeding. We recommend you to go through provided detailed analysis as below take decision accordingly.
Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet Breastfeeding Analsys
SafeCAS Number: 85721-33-1
Quinolone-related medication has been used in neonates and infants without known side effects. It is excreted in tiny amounts into breast milk. Absorption through the child’s gut may be interfered by calcium in the milk. Should it be prescribed to a nursing mother Norfloxacine, Ofloxacine and Ciprofloxacine are to be chosen since they have shown a lowest excretion into the milk. One case of pseudomembranose colitis, possibly related to mother ingestion of Ciporfloxacine, in a premature infant has been described who previously was affected of NEC, Follow-up for diarrhea in the infant is warranted. Be aware of false negative bacterial cultures in the infant when the mother is on antibiotics. The American Academy of Pediatrics rates it compatible with breastfeeding.
Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
CAS Number: 85721-33-1
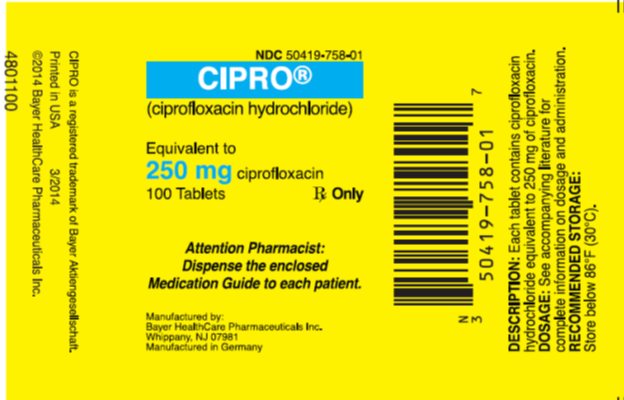
Amounts of ciprofloxacin in breastmilk are low. Fluoroquinolones such as ciprofloxacin have traditionally not been used in infants because of concern about adverse effects on the infants' developing joints. However, studies indicate little risk.[1] The calcium in milk might decrease absorption of the small amounts of fluoroquinolones in milk,[2] but, insufficient data exist to prove or disprove this assertion. Use of ciprofloxacin is acceptable in nursing mothers with monitoring of the infant for possible effects on the gastrointestinal flora, such as diarrhea or candidiasis (thrush, diaper rash). Avoiding breastfeeding for 3 to 4 hours after a dose should decrease the exposure of the infant to ciprofloxacin in breastmilk. Maternal use of an ear drop or eye drop that contains ciprofloxacin presents negligible risk for the nursing infant. To substantially diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue.
I am nursing mother and I have already used Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet, what should I do?
Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet is safe in breastfeeding and should not create any health problem for your baby but in case you feel any health issue associated with Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet you should contact your doctor or health care provider. Be it pregnancy or lactation you shall keep your doctor informed.
I am nursing mother and my doctor has suggested me to use Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet, is it safe?
Definitely, Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet is safe in lactation for baby. No wonder your doctor has recommended it.
If I am using Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet, will my baby need extra monitoring?
No extra baby monitoring required while mother is using Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Cipro floxacin Hydrochloride Tablet in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Drug Brands with same Active ingredients




