Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection while Breastfeeding
What is Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection used for?
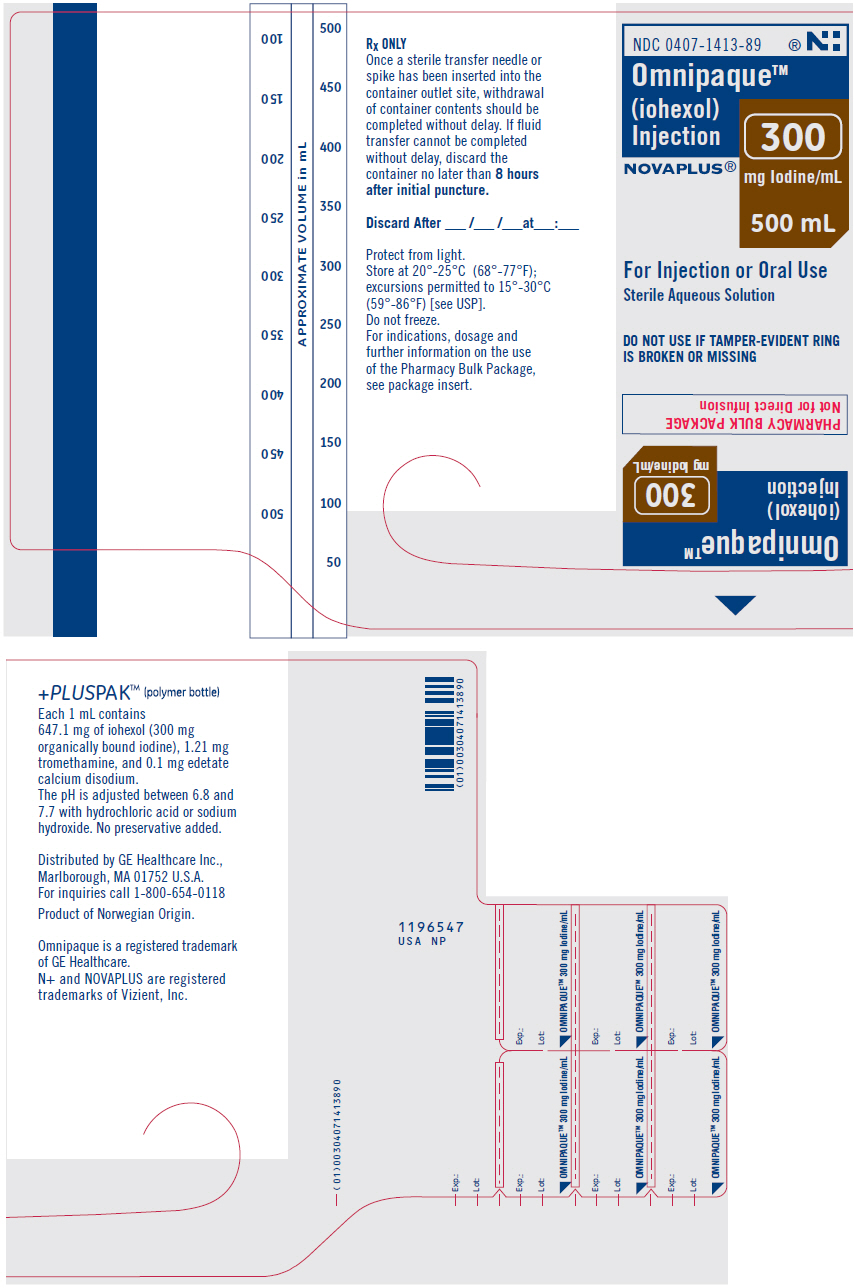
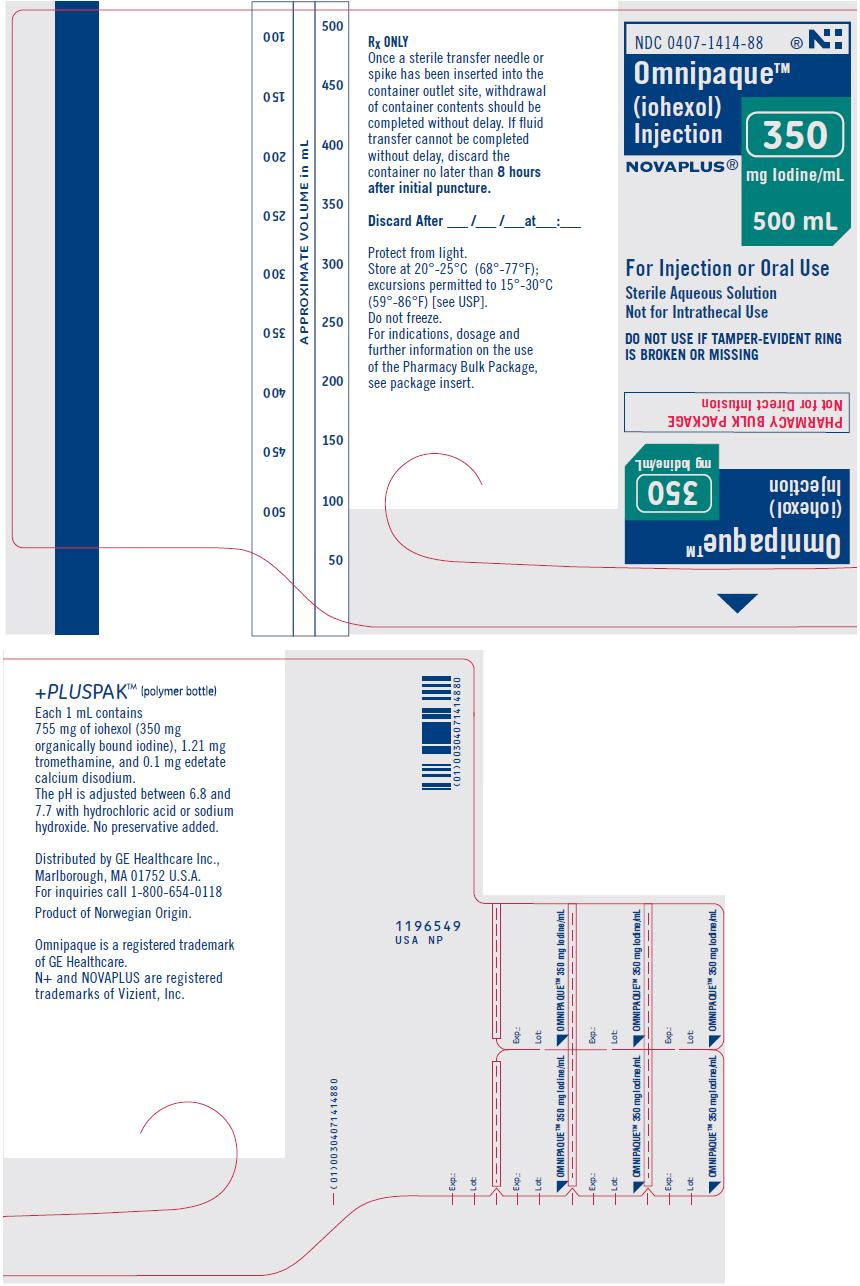
INDICATIONS AND USAGE GENERAL—Intravascular OMNIPAQUE 350 is indicated in adults for angiocardiography (ventriculography, selective coronary arteriography), aortography including studies of the aortic root, aortic arch, ascending aorta, abdominal aorta and its branches, intravenous digital subtraction angiography of the head, neck, abdominal, renal and peripheral vessels, peripheral arteriography, and excretory urography. OMNIPAQUE 350 is indicated in pediatric patients for angiocardiography (ventriculography, pulmonary arteriography, and venography; studies of the collateral arteries and aortography, including the aortic root, aortic arch, ascending and descending aorta). OMNIPAQUE 300 is indicated in adults for aortography including studies of the aortic arch, abdominal aorta and its branches, cerebral arteriography, peripheral venography (phlebography), and excretory urography. OMNIPAQUE 300 is indicated in pediatric patients for angiocardiography (ventriculography), excretory urography.
INDIVIDUAL INDICATIONS AND USAGE ANGIOCARDIOGRAPHY Pharmacology—Hemodynamic Changes OMNIPAQUE 350 at a concentration of 350 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in adults for angiocardiography (ventriculography, aortic root injections, and selective coronary arteriography). OMNIPAQUE 350 at a concentration of 350 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in pediatric patients for angiocardiography (ventriculography, pulmonary arteriography, and venography, and studies of the collateral arteries). OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in pediatric patients pediatric patients for angiocardiography (ventriculography). After both ventricular and coronary injection, decreases in systolic pressure were less pronounced and returned to baseline values earlier with OMNIPAQUE 350 than with diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium injection. OMNIPAQUE 350 produced less Q-T interval prolongation than seen with diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium injection. In pediatric patients, after injection of all sites, but particularly following ventricular and pulmonary artery injections, decreases in both systolic and diastolic intravascular pressure were significantly less pronounced with OMNIPAQUE 350 than with diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium injection. In pediatric patients OMNIPAQUE 350 produced significantly less shortening of the R-R interval than seen with diatrizoate meglumine and diatrizoate sodium injection. If repeat injections are made in rapid succession, all these changes are likely to be more pronounced. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.) Precautions During administration of large doses of OMNIPAQUE 350, continuous monitoring of vital signs is desirable. Caution is advised in the administration of large volumes to patients with incipient heart failure because of the possibility of aggravating the preexisting condition. Hypotension should be corrected promptly since it may induce serious arrhythmias. Special care regarding dosage should be observed in patients with right ventricular failure, pulmonary hypertension, or stenotic pulmonary vascular beds because of the hemodynamic changes which may occur after injection into the right heart outflow tract. (See PRECAUTIONS—General.) Pediatric patients at higher risk of experiencing adverse events during contrast medium administration may include those having asthma, a sensitivity to medication and/or allergens, congestive heart failure, a serum creatinine greater than 1.5 mg/dL or those less than 12 months of age. Adverse Reactions Cardiovascular system reactions in angiocardiography included angina (8%), hypotension (2.5%), bradycardia (1%), and tachycardia (1%). (See ADVERSE REACTIONS: Intravascular—General.) Dosage and Administration The individual dose or volume is determined by the size of the structure to be visualized, the anticipated degree of hemodilution, and valvular competence. Weight is a minor consideration in adults, but must be considered in infants and young pediatric patients. The volume of each individual injection is a more important consideration than the total dosage used. When large individual volumes are administered, as in ventriculography and aortography, it has been suggested that several minutes be permitted to elapse between each injection to allow for subsidence of possible hemodynamic disturbances. The recommended single injection volume of OMNIPAQUE 350 for angiocardiographic procedures in adults and the recommended single injection volumes of OMNIPAQUE 350 and OMNIPAQUE 300 for angiographic procedures in pediatric patients are as follows: Ventriculography Adults The usual adult volume for a single injection is 40 mL with a range of 30 mL to 60 mL. This may be repeated as necessary. When combined with selective coronary arteriography, the total administered volume should not exceed 250 mL (87.5 g Iodine). Pediatrics The usual single injection dose of OMNIPAQUE 350 is 1.25 mL/kg of body weight with a range of 1 mL/kg to 1.5 mL/kg. For OMNIPAQUE 300 the usual single injection dose is 1.75 mL/kg with a range of 1.5 mL/kg to 2.0 mL/kg. When multiple injections are given, the total administered dose should not exceed 5 mL/kg up to a total volume of 250 mL of OMNIPAQUE 350 or up to a total volume of 291 mL of OMNIPAQUE 300. Selective Coronary Arteriography The usual adult volume for right or left coronary arteriography is 5 mL (range 3 mL to 14 mL) per injection. Aortic Root and Arch Study When Used Alone The usual adult single injection volume is 50 mL, with a range of 20 mL to 75 mL. Pulmonary Angiography Pediatrics The usual single injection dose is 1 mL/kg of OMNIPAQUE 350. Combined Angiocardiographic Procedures Multiple Procedures Adults The visualization of multiple vascular systems and target organs is possible during a single radiographic examination of the patient. Large doses of OMNIPAQUE 350 were well tolerated in angiographic procedures requiring multiple injections. The maximum total volume for multiple procedures should not exceed 250 mL of 350 mg Iodine/mL (87.5 g Iodine). Pediatrics Visualization of multiple vascular systems and target organs is possible during a single radiographic examination of the patient. The maximum total dose for multiple injection procedures should not exceed 5 mL/kg up to a total volume of 250 mL of OMNIPAQUE 350 or 6 mL/kg up to a total volume of 291 mL of OMNIPAQUE 300. AORTOGRAPHY AND SELECTIVE VISCERAL ARTERIOGRAPHY OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL and OMNIPAQUE 350 at a concentration of 350 mg Iodine/mL are indicated in adults for use in aortography and selective visceral arteriography including studies of the aortic arch, ascending aorta, and abdominal aorta and its branches (celiac, mesenteric, renal, hepatic and splenic arteries). OMNIPAQUE 350 at a concentration of 350 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in pediatric patients for use in aortography including studies of the aortic root, aortic arch, ascending and descending aorta. Precautions Under conditions of slowed aortic circulation there is an increased likelihood for aortography to cause muscle spasm. Occasional serious neurologic complications, including paraplegia, have also been reported in patients with aortoiliac obstruction, femoral artery obstruction, abdominal compression, hypotension, hypertension, spinal anesthesia, and injection of vasopressors to increase contrast. In these patients the concentration, volume and number of repeat injections of the medium should be maintained at a minimum with appropriate intervals between injections. The position of the patient and catheter tip should be carefully monitored. Entry of a large aortic dose into the renal artery may cause, even in the absence of symptoms, albuminuria, hematuria, and an elevated creatinine and urea nitrogen. Rapid and complete return of function usually follows. (See PRECAUTIONS—General.) Adverse Reactions See ADVERSE REACTIONS: Intravascular—General, and ADVERSE REACTIONS ANGIOCARDIOGRAPHY. Dosage and Administration Adults The usual adult volume as a single injection is 50 mL to 80 mL for the aorta, 30 mL to 60 mL for major branches including celiac and mesenteric arteries, and 5 mL to 15 mL for renal arteries. Repeated injections may be performed if indicated, but the total volume should not exceed 291 mL of OMNIPAQUE 300 or 250 mL of OMNIPAQUE 350 (87.5 g Iodine). Pediatrics The usual single injection dose is 1.0 mL/kg of OMNIPAQUE 350 and should not exceed 5.0 mL/kg up to a total volume of 250 mL of OMNIPAQUE 350. CEREBRAL ARTERIOGRAPHY OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in adults for use in cerebral arteriography. The degree of pain and flushing as the result of the use of OMNIPAQUE 300 in cerebral arteriography is less than that seen with comparable injections of many contrast media. In cerebral arteriography, patients should be appropriately prepared consistent with existing or suspected disease states. Precautions Cerebral arteriography should be undertaken with extreme care with special caution in elderly patients, patients in poor clinical condition, advanced arteriosclerosis, severe arterial hypertension, recent cerebral embolism or thrombosis, and cardiac decompensation. Since the contrast medium is given by rapid injection, the patient should be monitored for possible untoward reactions. (See PRECAUTIONS—General.) Adverse Reactions Cerebral arteriography with water-soluble contrast media has been associated with temporary neurologic complications including seizures, drowsiness, transient paresis, and mild disturbances in vision such as photomas of 1-second or less duration. Central nervous system reactions in cerebral arteriography included photomas (15%), headache (5.5%), and pain (4.5%). (See ADVERSE REACTIONS: Intravascular—General.) Dosage and Administration OMNIPAQUE 300 is recommended for cerebral arteriography at the following volumes: common carotid artery (6 mL to 12 mL), internal carotid artery (8 mL to 10 mL), external carotid artery (6 mL to 9 mL), and vertebral artery (6 mL to 10 mL). DIGITAL SUBTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY Intravenous Administration OMNIPAQUE 350 at a concentration of 350 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in adults for use in intravenous digital subtraction angiography (I.V.DSA) of the vessels of the head, neck, and abdominal, renal and peripheral vessels. Arteriograms of diagnostic quality can be obtained following the intravenous administration of contrast media employing digital subtraction and computer imaging enhancement techniques. The intravenous route of administration using these techniques has the advantage of being less invasive than the corresponding selective catheter placement of medium. The dose is administered into a peripheral vein, the superior vena cava or right atrium, usually by mechanical injection although sometimes by rapid manual injection. The technique has been used to visualize the ventricles, aorta and most of its larger branches, including the carotids, cerebrals, vertebrals, renal, celiac, mesenterics, and the major peripheral vessels of the limbs. Radiographic visualization of these structures is possible until significant hemodilution occurs. OMNIPAQUE 350 can be injected intravenously as a rapid bolus to provide arterial visualization using digital subtraction radiography. Preprocedural medications are not considered necessary. OMNIPAQUE 350 has provided diagnostic arterial radiographs in about 95% of patients. In some cases, poor arterial visualization has been attributed to patient movement. OMNIPAQUE 350 is very well tolerated in the vascular system. Patient discomfort (general sensation of heat and/or pain) following injection is less than with various other contrast media. Precautions Since the contrast medium is usually administered mechanically under high pressure, rupture of smaller peripheral veins can occur. It has been suggested that this can be avoided by using an intravenous catheter threaded proximally beyond larger tributaries or, in the case of the antecubital vein, into the superior vena cava. Sometimes the femoral vein is used. (See PRECAUTIONS—General.) Adverse Reactions Cardiovascular system reactions in digital arteriography included transient PVCs (16%) and PACs (6.5%). (See ADVERSE REACTIONS: Intravascular—General.) Dosage and Administration The usual injection volume of OMNIPAQUE 350 for the intravenous digital technique is 30 mL to 50 mL of a 350 mg Iodine/mL solution. This is administered as a bolus at 7.5 to 30 mL/second using a pressure injector. The volume and rate of injection will depend primarily on the type of equipment and technique used. Frequently three or more injections may be required, up to a total volume not to exceed 250 mL (87.5 g Iodine). PERIPHERAL ANGIOGRAPHY OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL or OMNIPAQUE 350 at a concentration of 350 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in adults for use in peripheral arteriography. OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in adults for use in peripheral venography. Sedative medication may be employed prior to use. Anesthesia is not considered necessary. Patient discomfort during and immediately following injection is substantially less than that following injection of various other contrast media. Moderate to severe discomfort is very unusual. Precautions Pulsation should be present in the artery to be injected. In thromboangiitis obliterans, or ascending infection associated with severe ischemia, angiography should be performed with extreme caution, if at all. (See PRECAUTIONS—General.) Adverse Reactions A transient sensation of mild warmth is usual, immediately following injection. This has not interfered with the procedure. In phlebography the incidence of leg pain was 21%. This usually was mild and lasted a short time after injection. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS: Intravascular—General.) Dosage and Administration The volume required will depend on the size, flow rate, and disease state of the injected vessel and on the size and condition of the patient, as well as the imaging technique used. The dosage recommended for use in peripheral angiography is as follows: Aortofemoral runoffs: 20 mL to 70 mL of OMNIPAQUE 350 (350 mg Iodine/mL) 30 mL to 90 mL of OMNIPAQUE 300 (300 mg Iodine/mL) Selective arteriograms: (femoral/iliac) 10 mL to 30 mL of OMNIPAQUE 350 (350 mg Iodine/mL) 10 mL to 60 mL of OMNIPAQUE 300 (300 mg Iodine/mL) Venography (per leg): 40 mL to 100 mL of OMNIPAQUE 300 (300 mg Iodine/mL) EXCRETORY UROGRAPHY OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL or OMNIPAQUE 350 at a concentration of 350 mg Iodine/mL is indicated for use in adults in excretory urography to provide diagnostic contrast of the urinary tract. OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in pediatric patients for excretory urography. (See Section III for information on voiding cystourethrography.) For pharmacokinetics of excretion in adults, see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY—Intravascular. Precautions Preparatory dehydration is not recommended in the elderly, pediatric patients, diabetic or azotemic patients, or in patients with suspected myelomatosis. Pediatric patients at higher risk of experiencing adverse events during contrast medium administration may include those having asthma, a sensitivity to medication and/or allergens, congestive heart failure, a serum creatinine greater than 1.5 mg/dL or those less than 12 months of age. Since there is a possibility of temporary suppression of urine formation, it is recommended that a suitable interval elapse before excretory urography is repeated, especially in patients with unilateral or bilateral reduction in renal function. (See PRECAUTIONS—General.) Adverse Reactions See ADVERSE REACTIONS: Intravascular—General. Dosage and Administration Adults OMNIPAQUE 300 and OMNIPAQUE 350 at dosages from 200 mg Iodine/kg body weight to 350 mg Iodine/kg body weight have produced diagnostic opacification of the excretory system in patients with normal renal function. Pediatrics Excretory Urography OMNIPAQUE 300 at doses of 0.5 mL/kg to 3 mL/kg of body weight has produced diagnostic opacification of the excretory tract. The usual dose for pediatric patients is 1 mL/kg to 1.5 mL/kg. Dosage for pediatric patients should be administered in proportion to age and body weight. The total administered dose should not exceed 3 mL/kg.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE, GENERAL—Oral/Body Cavity Use OMNIPAQUE 300 and OMNIPAQUE 350 have osmolalities from approximately 2.4 to 3 times that of plasma (285 mOsm/kg water) and are hypertonic under conditions of use. Adults OMNIPAQUE 350 is indicated in adults for arthrography and oral pass-thru examination of the gastrointestinal tract. OMNIPAQUE 300 is indicated in adults for arthrography and hysterosalpingography. OMNIPAQUE diluted to concentrations from 6 mg Iodine/mL to 9 mg Iodine/mL administered orally in conjunction with OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL administered intravenously is indicated in adults for contrast enhanced computed tomography of the abdomen. Pediatric Patients OMNIPAQUE 300 is indicated in pediatric patients for examination of the gastrointestinal tract. OMNIPAQUE diluted to concentrations from 50 mg Iodine/mL to 100 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in pediatric patients for voiding cystourethrography. OMNIPAQUE diluted to concentrations from 9 mg Iodine/mL to 21 mg Iodine/mL administered orally in conjunction with OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL administered intravenously are indicated in pediatric patients for use in contrast enhanced computed tomography of the abdomen.
INDIVIDUAL INDICATIONS AND USAGE Oral Use Adults OMNIPAQUE 350 at a concentration of 350 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in adults for use in oral pass-thru examination of the gastrointestinal tract. OMNIPAQUE diluted to concentrations from 6 mg Iodine/mL to 9 mg Iodine/mL administered orally in conjunction with OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL administered intravenously are indicated in adults for use in contrast enhanced computed tomography of the abdomen. Dilute oral plus intravenous OMNIPAQUE may be useful when unenhanced imaging does not provide sufficient delineation between normal loops of the bowel and adjacent organs or areas of suspected pathology. Pediatric patients OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL administered orally or rectally is indicated in pediatric patients for use in examination of the gastrointestinal tract. OMNIPAQUE diluted to concentrations from 9 mg Iodine/mL to 21 mg Iodine/mL administered orally in conjunction with OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL administered intravenously are indicated in pediatric patients for use in contrast enhanced computed tomography of the abdomen. Precautions See PRECAUTIONS—General. Adverse Reactions Oral administration of OMNIPAQUE is most often associated with mild, transient diarrhea especially when high concentrations and large volumes are administered. Nausea, vomiting, and moderate diarrhea have also been reported following orally administered OMNIPAQUE, but much less frequently. For CT examinations using dilute oral plus intravenous contrast medium, adverse events are more likely to be associated with the intravenous injection than the hypotonic oral solution. It should be noted that serious or anaphylactoid reactions that may occur with intravascular iodinated media are possible following administration by other routes. Adults In controlled clinical trials involving 54 adult patients for oral pass-thru examination of the gastrointestinal tract using OMNIPAQUE 350, the following adverse reactions were reported: diarrhea (42%), nausea (15%), vomiting (11%), abdominal pain (7%), flatulence (2%), and headache (2%). In controlled clinical studies involving 44 adult patients for dilute oral plus intravenous CT examination of the gastrointestinal tract using OMNIPAQUE 300, adverse reactions were limited to a single report of vomiting (2%). Pediatric patients In controlled clinical studies involving 58 pediatric patients for examination of the gastrointestinal tract at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL, the following adverse reactions were reported: diarrhea (36%), vomiting (9%), nausea (5%), fever (5%), hypotension (2%), abdominal pain (2%), and urticaria (2%). In clinical studies an increased frequency and severity of diarrhea was noted with an increase in the administered concentration and dose of the radiocontrast agent. In controlled clinical studies involving 69 pediatric patients for dilute oral plus intravenous CT examination of the gastrointestinal tract using OMNIPAQUE 300, adverse reactions were limited to a single report of vomiting (1.4%). Dosage and Administration Adults The recommended dosage of undiluted OMNIPAQUE 350 at a concentration of 350 mg Iodine/mL for oral pass-thru examination of the gastrointestinal tract in adults is 50 mL to 100 mL depending on the nature of the examination and the size of the patient. The recommended oral dosage of OMNIPAQUE diluted to concentrations of 6 mg Iodine/mL to 9 mg Iodine/mL for contrast enhanced computed tomography of the abdomen in adults is 500 mL to 1000 mL. Smaller administered volumes are needed as the concentration of the final solution is increased (see Table below). In conjunction with dilute oral administration, the recommended dosage of OMNIPAQUE 300 intravenously is 100 mL to 150 mL. The oral dose is administered about 20 to 40 minutes prior to the intravenous dose and image acquisition. Pediatric Patients The dosage of undiluted OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL, is dependent on the nature of the examination and the size of the patient. Based on clinical experience, it is recommended that OMNIPAQUE 180 (available in single use vials), be used in pediatric patients less than 3 months of age. OMNIPAQUE 300 may be used in pediatric patients 3 months of age and older. The following dosage guidelines are recommended: Age Volume of OMNIPAQUE Less than 3 months 5 — 30 mL Three months to 3 years Up to 60 mL Four years to 10 years Up to 80 mL Greater than 10 years Up to 100 mL When given rectally, larger volumes may be used. The recommended oral dosage of OMNIPAQUE diluted to concentrations of 9 mg Iodine/mL to 21 mg Iodine/mL for contrast computed tomography of the abdomen in pediatric patients is 180 mL to 750 mL. Smaller administered volumes are needed as the concentration of the final solution is increased (see Table below). The total oral dose in grams of iodine should generally not exceed 5 g Iodine for pediatric patients under 3 years of age and 10 g Iodine for pediatric patients from 3 to 18 years of age. The oral dosage may be given all at once or over a period of 30 to 45 minutes if there is difficulty in consuming the required volume. In conjunction with dilute oral administration the recommended dosage of OMNIPAQUE 300 is 2mL/kg when administered intravenously with a range of 1 mL/kg to 2 mL/kg. Dosage pediatric patients should be administered in proportion to age and body weight. The total intravenously administered dose should not exceed 3 mL/kg. The oral dose is administered about 30 to 60 minutes prior to the intravenous dose and image acquisition. OMNIPAQUE may be diluted with water or beverage as follows: To Achieve Add To One Liter of Contrast Medium at A Final Concentration (mg Iodine/mL) of Stock Concentration of OMNIPAQUE (mg Iodine/mL) Volume (mL) Water, Carbonated Beverage, Milk, or Juice (mL) 6 300 20 980 350 17 983 9 300 30 970 350 26 974 12 300 40 960 350 35 965 15 300 50 950 350 43 957 18 300 60 940 350 52 948 21 300 70 930 350 60 940 Dilutions of OMNIPAQUE should be prepared just prior to use and any unused portion discarded after the procedure. VOIDING CYSTOURETHROGRAPHY (VCU) OMNIPAQUE diluted to concentrations from 50 mg Iodine/mL to 100 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in pediatric patients for voiding cystourethrography. VCUs are often performed in conjunction with excretory urography. Precautions See PRECAUTIONS—General. Since the VCU procedure requires instrumentation, special precautions should be observed in those patients known to have an acute urinary tract infection. Filling of the bladder should be done at a steady rate, exercising caution to avoid excessive pressure. Sterile procedures are essential. Adverse Reactions See ADVERSE REACTIONS—General. Dosage and Administration OMNIPAQUE may be diluted, utilizing aseptic technique, with Sterile Water for Injection to a concentration of 50 mg Iodine/mL to 100 mg Iodine/mL for voiding cystourethrography. The concentration may vary depending upon the patient's size and age and also with the technique and equipment used. Sufficient volume of contrast medium should be administered to adequately fill the bladder. The usual volume ranges from 50 mL to 300 mL of OMNIPAQUE at a concentration of 100 mg Iodine/mL and 50 mL to 600 mL of OMNIPAQUE at a concentration of 50 mg Iodine/mL. OMNIPAQUE may be diluted with Sterile Water for Injection as indicated in the table below: To Achieve Add To A Final Concentration Each 100 mL of OMNIPAQUE Sterile Water for Injection, USP (mL) (mg Iodine/mL) OMNIPAQUE 300 OMNIPAQUE 350 100 200 250 90 233 289 80 275 338 70 330 400 60 400 483 50 500 600 Dilutions of OMNIPAQUE should be prepared just prior to use and any unused portion discarded after the procedure. ARTHROGRAPHY OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL or OMNIPAQUE 350 at a concentration of 350 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in radiography of the knee joint in adults, and OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in radiography of the shoulder joint in adults, and OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in radiography of the temporomandibular joint in adults. Arthrography may be helpful in the diagnosis of posttraumatic or degenerative joint diseases, synovial rupture, the visualization of communicating bursae or cysts, and in meniscography. Precautions See PRECAUTIONS—General. Strict aseptic technique is required to prevent infection. Fluoroscopic control should be used to ensure proper needle placement, prevent extracapsular injection, and prevent dilution of contrast medium. Undue pressure should not be exerted during injection. Adverse Reactions Injection of OMNIPAQUE into the joint is associated with transient discomfort, ie, pain, swelling. However, delayed, severe or persistent discomfort may occur occasionally. Severe pain may often result from undue use of pressure or the injection of large volumes. Joint swelling after injection is less with OMNIPAQUE than with high osmolar ionic contrast medium. These types of reactions are generally procedurally dependent and of greater frequency when double-contrast technique is employed. Nervous system: Swelling sensation (42%), pain (29%), heat sensation (13%), and muscle weakness (0.7%). Skin and appendages: Hematoma at injection site (0.7%). Dosage and Administration Arthrography is usually performed under local anesthesia. The amount of OMNIPAQUE injected is dependent on the size of the joint to be examined and the technique employed. Lower volumes of contrast medium are usually injected for knee and shoulder arthrography when double-contrast examinations using 15 mL to 100 mL of air are performed. The following concentrations and volumes are recommended for normal adult knee, shoulder, and temporomandibular joints but should serve as guidelines since joints may require more or less contrast medium for optimal visualization. KNEE OMNIPAQUE 300 5 mL to 15 mL OMNIPAQUE 350 5 mL to 10 mL Lower volumes recommended for double-contrast examinations; higher volumes recommended for single-contrast examinations. SHOULDER OMNIPAQUE 300 10 mL TEMPOROMANDIBULAR OMNIPAQUE 300 0.5 mL to 1 mL Passive or active manipulation is used to disperse the medium throughout the joint space. Figure HYSTEROSALPINGOGRAPY OMNIPAQUE 300 at a concentration of 300 mg Iodine/mL is indicated in radiography of the internal group of adult female reproductive organs; ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina. Hysterosalpingography is utilized as a diagnostic and therapeutic modality in the treatment of infertility and other abnormal gynecological conditions. Contraindications The procedure should not be performed during the menstrual period or when menstrual flow is imminent, nor should it be performed when infection is present in any portion of the genital tract, including the external genitalia. The procedure is also contraindicated for pregnant women or for those in whom pregnancy is suspected. Its use is not advised for 6 months after termination of pregnancy or 30 days after conization or curettage. Precautions In patients with carcinoma or in those in whom the condition is suspected, caution should be exercised to avoid possible spreading of the lesion by the procedure. Adverse Reactions Injection of OMNIPAQUE in hysterosalpingography is associated with immediate but transient pain. The cause of the pain may be due as much to the procedure itself as to the contrast medium injected, therefore attention should be paid to the injection pressure and volume instilled to avoid disruptive distention of the uterus and fallopian tubes. Fluoroscopic monitoring is recommended. Nervous system: Pain (49%), somnolence and fever each with an individual incidence of 3%. Gastrointestinal system: Nausea (3%). Dosage and Administration The recommended dosage of OMNIPAQUE 300 is 15 mL to 20 mL but will vary depending on individual anatomy and/or disease state.
I am breastfeeding mother and I am using Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection. Can it have any bad effect on my kid? Shall I search for better alternative?

Nursing Mothers It is not known to what extent iohexol is excreted in human milk. However, many injectable contrast agents are excreted unchanged in human milk. Although it has not been established that serious adverse reactions occur in nursing infants, caution should be exercised when intravascular contrast media are administered to nursing women. Bottle feedings may be substituted for breast feedings for 24 hours following administration of OMNIPAQUE.
Nursing Mothers It is not known to what extent iohexol is excreted in human milk. However, many injectable contrast agents are excreted unchanged in human milk. Although it has not been established that serious adverse reactions occur in nursing infants, caution should be exercised when intravascular contrast media are administered to nursing women. Bottle feedings may be substituted for breast feedings for 24 hours following administration of OMNIPAQUE.
Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection Breastfeeding Analsys
Iodine while Breastfeeding
UnsafeCAS Number: 7553-56-2
Disinfectant that contains high amount (2-7%) of Iodine in solution with alcohol or water (Lugol's solution) Not absorbed through intact skin of adults. However, it may trespass the inflamed skin, wounds, mucosa surfaces like vagina, in which case can reach concentration in grams in the human serum (1 g = 1,000 milligrams = 1,000,000 micrograms). Normal daily allowance is considered to be as high as 100 to 150 micrograms that increases to 200 – 300 micrograms in pregnancy or nursing period. The latter means less than one third of a milligram. Iodine is concentrated into breast milk with a level that could reach 20 times higher than the concentration in the blood. It has been found higher levels of Iodine, altered results of neonatal screening test for thyroid function, and, transient hypothyroidism in infants whose mothers were exposed to Iodine Povidone. Use should be avoid in the Delivery Room, Operating Room (C-section), Neonatal Units, Toddler admision areas and during the breastfeeding period. Sporadic or inadvertent use, specially on normal skin, does not require special test or procedures because it does not pose higher risk to the child.
Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Iodine while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 7553-56-2
Iodine is an essential trace nutrient for all infants that a normal component of breastmilk. Infant requirements are estimated to be 15 mcg/kg daily in fullterm infants and 30 mcg/kg daily in premature infants.[1] Systematic reviews and studies on iodine nutrition found that iodine in breastmilk is adequate in iodine-sufficient countries, but in countries with iodine fortification of foods, many mothers did not obtain adequate iodine and that additional supplementation was desirable.[2][3][4][5] In iodine-deficient areas, supplementation of breastfeeding mothers with iodine appears to be more effective than direct supplementation of the infant in reducing infant iodine deficiency.[6] The American Thyroid Association recommends that breastfeeding women should supplement their diet with a daily oral supplement that contains 150 mcg of iodine, but sustained iodine intake while breastfeeding that exceeds 500 to 1100 mcg daily should be avoided.[7] A survey in the United States between 2011 and 2014 found that only 19% of lactating women used a dietary supplement that contained iodine.[8] The use of excessive amounts of iodine in the mother near term and during breastfeeding (e.g., seaweed soup) can increase breastmilk iodine levels and cause transient hypothyroidism in breastfed infants. The absorption of iodine can be marked after application to open wounds or mucous membranes. Exposure of mothers to unnecessary iodine who are or will be breastfeeding should be avoided or minimized to the extent possible by avoiding its use on maternal mucous membranes (e.g., vaginal use, wound therapy), avoiding prolonged contact time, avoiding repeated applications, and applying it to the smallest possible surface areas of the body. It is possible that maternal exposure to iodine near term could interfere with thyroid studies done as a part of newborn screening tests.
What should I do if I am breastfeeding mother and I am already exposed to Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection?
If you observer abnormal behavior or any other health issue in infant then you should immediately call 911 or contact other contact other emergency service provider in your area otherwise closely monitor the baby and inform your doctor about your Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection usage and time interval of breastfeeding.
I am nursing mother and my doctor has suggested me to use Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection, is it safe?
If your doctor knows that you are breastfeeding mother and still prescribes Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection then there must be good reason for that as Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection is considered unsafe, It usually happens when doctor finds that overall advantage of taking
If I am using Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Yes, Extra monitoring is required if mother is using Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection and breastfeeding as it is considered unsafe for baby.
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Omnipaque | Iohexol Injection in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
