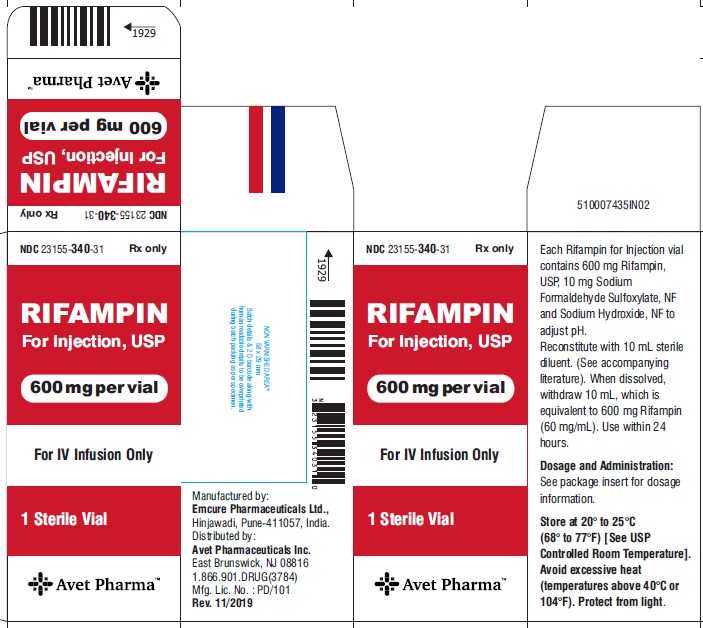
Nutrients from the food that you eat passes to your breast milk. Its good idea to take healthy diet while breastfeeding. You may need to consume more calories per day to support healthy body system. Some time it gets necessary take medicine while you are breastfeeding and as other food items passes into breast milk, medicine passes as well hence it becomes obvious to understand its effects while breastfeeding. We have analyzed many medications and in this sheet we will present some fact and known information associated with Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution while breast-feeding.
What is Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution used for?
In the treatment of both tuberculosis and the meningococcal carrier state, the small number of resistant cells present within large populations of susceptible cells can rapidly become the predominant type. Bacteriologic cultures should be obtained before the start of therapy to confirm the susceptibility of the organism to rifampin and they should be repeated throughout therapy to monitor the response to treatment. Since resistance can emerge rapidly, susceptibility tests should be performed in the event of persistent positive cultures during the course of treatment. If test results show resistance to rifampin and the patient is not responding to therapy, the drug regimen should be modified. Tuberculosis Rifampin is indicated in the treatment of all forms of tuberculosis. A three-drug regimen consisting of rifampin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide (e.g., RIFATER®) is recommended in the initial phase of short-course therapy which is usually continued for 2 months. The Advisory Council for the Elimination of Tuberculosis, the American Thoracic Society, and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that either streptomycin or ethambutol be added as a fourth drug in a regimen containing isoniazid (INH), rifampin, and pyrazinamide for initial treatment of tuberculosis unless the likelihood of INH resistance is very low. The need for a fourth drug should be reassessed when the results of susceptibility testing are known. If community rates of INH resistance are currently less than 4%, an initial treatment regimen with less than four drugs may be considered. Following the initial phase, treatment should be continued with rifampin and isoniazid (e.g., RIFAMATE®) for at least 4 months. Treatment should be continued for longer if the patient is still sputum or culture positive, if resistant organisms are present, or if the patient is HIV positive. Rifampin for injection is indicated for the initial treatment and retreatment of tuberculosis when the drug cannot be taken by mouth. Meningococcal Carriers Rifampin is indicated for the treatment of asymptomatic carriers of Neisseria meningitidis to eliminate meningococci from the nasopharynx. Rifampin is not indicated for the treatment of meningococcal infection because of the possibility of the rapid emergence of resistant organisms. (See WARNINGS.) Rifampin should not be used indiscriminately, and therefore, diagnostic laboratory procedures, including serotyping and susceptibility testing, should be performed for establishment of the carrier state and the correct treatment. So that the usefulness of rifampin in the treatment of asymptomatic meningococcal carriers is preserved, the drug should be used only when the risk of meningococcal disease is high. To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of rifampin and other antibacterial drugs, rifampin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Is Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution safe to use while breastfeeding? Can it interfere with growth and development of my kid?
Rifampin is the only one ingredient used in manufacturing of Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution, Which makes it easier to analyze its effect in breastfeeding. As per our analysis of Rifampin it is safe to use Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution while lactating. We suggest you to check further details below about Rifampin usage in breastfeeding.
Statement of Manufacturer/Labeler about breastfeeding usage
Nursing Mothers Because of the potential for tumorigenicity shown for rifampin in animal studies, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution Breastfeeding Analsys
SafeCAS Number: 13292-46-1
It is excreted into breast milk in clinically non-significant amount, in fact a much lower amount than the dose used for the treatment or prophylaxis of infection in neonates and infants. Even more, no problems that would be attributable to rifampicin have been observed among infants whose mothers were taking this medication. It can cause an orange discoloration of body fluids, including the mother’s milk.Take into account possible negative results in bacterial cultures of febrile infants, when their mothers are on antibiotics. American Academy of Pediatrics states that it is usually compatible with breastfeeding medication.WHO List of Essential Medicines 2002: compatible with breastfeeding.
Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
CAS Number: 13292-46-1
Limited information indicates that there are low levels of rifampin in breastmilk that would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. The amount of rifampin in milk is insufficient to treat tuberculosis in the breastfed infant. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other professional organizations state that breastfeeding should not be discouraged in women taking rifampin.[1][2][3]
I am nursing mother and I have already used Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution, what should I do?
It is always a good idea to keep your healthcare provider or doctor informed about your drug usage during pregnancy and breastfeeding but if you have not informed your doctor about Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution and have used it then do not panic as Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution is mostly safe in breastfeeding and should not cause any harm to your baby.
My health care provider has asked me to use Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution, what to do?
Usage of Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution is safe for nursing mothers and baby, No worries.
If I am using Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution, will my baby need extra monitoring?
No
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Rifampin Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week