Imbue Pain Relief | Menthol - Methyl Salicylate Patch while Breastfeeding

What is Imbue Pain Relief | Menthol - Methyl Salicylate Patch used for?
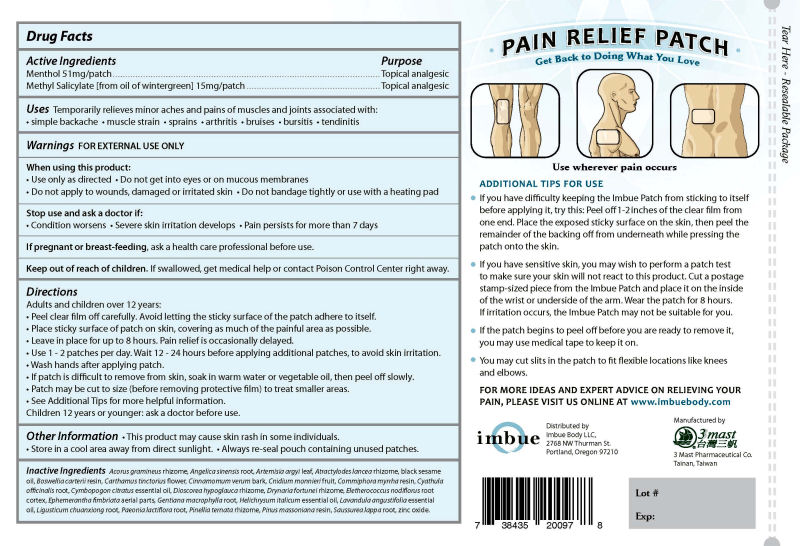
Brief: Topical Analgesic Topical Analgesic
Is Imbue Pain Relief | Menthol - Methyl Salicylate Patch safe to use while breastfeeding? Can it interfere with growth and development of my kid?

Imbue Pain Relief | Menthol - Methyl Salicylate Patch Breastfeeding Analsys
Menthol while Breastfeeding
SafeHerb which is widely used by many cultures. It has been used even for pain relief during pregnancy and colicky pain in fussy babies (without proved data on this). Since it is non toxic at appropriate dose and a tiny excretion into breast milk of active metabolite Menthol, a moderate consumption is believed compatible while breastfeeding. Dessicated leaves and essential oil of the plant that contains Menthol are used. Properties that have been demonstrated and approved indications are: as spasmolytic for Dyspepsia, Irritable Colon and flatulence. It has been used for the treatment of cracked nipple with best results than placebo or Lanolin. Although with no proven effectiveness, it is traditionally used for cough relief, common cold, pain or itching by local application or inhalation. Overdosing of essential oil may be harmful. Do not expose infants to inhalation of products that contain Menthol (irritation of the air way) In case of use on the nipple, do it after feeding the baby and cleanse thoroughly the surface before the next one.
Methyl salicylate while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 69-72-7
It is topically used as a keratolytic, antiseptic, antifungal, dermatological and stomatological agent. At last update no published data on excretion into breast milk were found . Systemic absorption (distribution into the body) depends on the concentration of the product used and the duration of application. Absorption may reach 10 to 25% of the total amount applied on the skin. It is recommended not to use during lactation in large areas of skin or for prolonged periods. Available data on the elimination of Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin-ASA) in breast milk indicates it is clinically insignificant.No cases have been reported on Reye's syndrome by ASA through the breast milk which is considered very unlikely to occur with isolated and/or small doses used as antithrombotic treatments and anti-abortion measures, even less after application on the skin or topically in the mouth. Do not apply on the breast to prevent ingestion by the infant. If necessary, apply it after the feed and wipe it off thoroughly with water before the next feed.
Imbue Pain Relief | Menthol - Methyl Salicylate Patch Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Menthol while Breastfeeding
Peppermint (Mentha x piperita) contains menthol, menthone, menthyl acetate as major ingredients. Minor ingredients include 1,8-cineole, pulegone, bitter substances, caffeic acid, flavonoids, and tannins. Peppermint is a purported galactogogue; however, no scientifically valid clinical trials support this use.[1] Galactogogues should never replace evaluation and counseling on modifiable factors that affect milk production.[2] Topical peppermint gel and solutions have been studied for the prevention of pain and cracked nipples and areolas in nursing women. The peppermint preparations were more effective than placebo and expressed breastmilk, and about as effective as lanolin,[3][4][5][6] although a meta-analysis concluded that application of nothing or breastmilk may be superior to lanolin, but good studies are lacking.[7] Menthol is excreted into breastmilk in small quantities; the excretion of other components have not been studied. Peppermint is "generally recognized as safe" (GRAS) as a food by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Large doses can cause heartburn, nausea and vomiting. Allergic reactions, including headache, have been reported to menthol. If peppermint is used on the nipples, it should be used after nursing and wiped off before the next nursing. Dietary supplements do not require extensive pre-marketing approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Manufacturers are responsible to ensure the safety, but do not need to the safety and effectiveness of dietary supplements before they are marketed. Dietary supplements may contain multiple ingredients, and differences are often found between labeled and actual ingredients or their amounts. A manufacturer may contract with an independent organization to verify the quality of a product or its ingredients, but that does certify the safety or effectiveness of a product. Because of the above issues, clinical testing results on one product may not be applicable to other products. More detailed information #about dietary supplements# is available elsewhere on the LactMed Web site.
Methyl salicylate while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 69-72-7
No information is available on the clinical use of salicylic acid on the skin during breastfeeding. Because it is unlikely to be appreciably absorbed or appear in breastmilk, it is considered safe to use during breastfeeding.[1] Avoid application to areas of the body that might come in direct contact with the infant's skin or where the drug might be ingested by the infant via licking.
I am nursing mother and I have already used Imbue Pain Relief | Menthol - Methyl Salicylate Patch, what should I do?
As usage of Imbue Pain Relief | Menthol - Methyl Salicylate Patch is mostly safe while breastfeeding hence there should not be any concern. In case of any change in behavior or health of your baby you should inform your health care provider about usage of Imbue Pain Relief | Menthol - Methyl Salicylate Patch else no further action is required.
My health care provider has asked me to use Imbue Pain Relief | Menthol - Methyl Salicylate Patch, what to do?
Usage of Imbue Pain Relief | Menthol - Methyl Salicylate Patch is safe for nursing mothers and baby, No worries.
If I am using Imbue Pain Relief | Menthol - Methyl Salicylate Patch, will my baby need extra monitoring?
No
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Imbue Pain Relief | Menthol - Methyl Salicylate Patch in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
