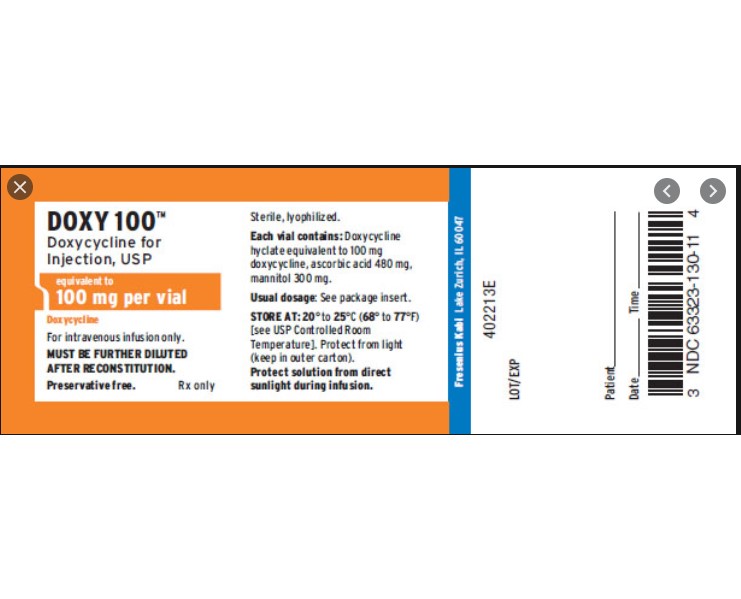
Breast milk is superior in nutrition, It provides resistance against infections and allergies, It is naturally sterile. Despite all the advantages of breastfeeding some mothers choose to pause the breastfeeding in fear of harmful effects of medicines passing in breast milk. Are you wondering about breastfeeding and using Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution ? Know what is Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution and how it can affect your breast milk and whether Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution is safe for your kid or not.
What is Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution used for?
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Doxycycline for Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Doxycycline for Injection, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy. Doxycycline for Injection, USP is indicated in infections caused by the following microorganisms: Rickettsiae (Rocky Mountain spotted fever, typhus fever, and the typhus group, Q fever, rickettsial pox and tick fevers). Mycoplasma pneumoniae (PPLO, Eaton Agent). Agents of psittacosis and ornithosis. Agents of lymphogranuloma venereum and granuloma inguinale. The spirochetal agent of relapsing fever (Borrelia recurrentis). The following gram-negative microorganisms: Haemophilus ducreyi (chancroid). Yersinia pestis (formerly Pasteurella pestis) and Francisella tularensis (formerly Pasteurella tularensis). Bartonella bacilliformis. Bacteroides species. Vibrio cholerae (formerly Vibrio comma) and Campylobacter fetus (formerly Vibrio fetus). Brucella species (in conjunction with streptomycin). Because many strains of the following groups of microorganisms have been shown to be resistant to tetracyclines, culture and susceptibility testing are recommended. Doxycycline is indicated for treatment of infections caused by the following gram-negative microorganisms when bacteriologic testing indicates appropriate susceptibility to the drug: Escherichia coli. Enterobacter aerogenes (formerly Aerobacter aerogenes). Shigella species. Acinetobacter species (formerly Mima species and Herellea species). Haemophilus influenzae (respiratory infections). Klebsiella species (respiratory and urinary infections). Doxycycline is indicated for treatment of infections caused by the following gram-positive microorganisms when bacteriologic testing indicates appropriate susceptibility to the drug: Streptococcus species: Up to 44 percent of strains of Streptococcus pyogenes and 74 percent of Enterococcus faecalis (formerly Streptococcus faecalis) have been found to be resistant to tetracycline drugs. Therefore, tetracyclines should not be used for streptococcal disease unless the organism has been demonstrated to be sensitive. For upper respiratory infections due to group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, penicillin is the usual drug of choice, including prophylaxis of rheumatic fever. Streptococcus pneumoniae (formerly Diplococcus pneumoniae). Staphylococcus aureus, respiratory, skin and soft tissue infections. Tetracyclines are not the drugs of choice in the treatment of any type of staphylococcal infections. Anthrax due to Bacillus anthracis, including inhalational anthrax (post-exposure): to reduce the incidence or progression of disease following exposure to aerosolized Bacillus anthracis. When penicillin is contraindicated, doxycycline is an alternative drug in the treatment of infections due to: Neisseria gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis. Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue (syphilis and yaws). Listeria monocytogenes. Clostridium species. Fusobacterium fusiforme (Vincent's infection). Actinomyces species. In acute intestinal amebiasis, doxycycline may be a useful adjunct to amebicides. Doxycycline is indicated in the treatment of trachoma, although the infectious agent is not always eliminated, as judged by immunofluorescence.
Is using Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution safe or dangerous while breastfeeding?
Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution contains only one active ingredient that is Doxycycline anhydrous. We have analyzed the usage of Doxycycline anhydrous in breastfeeding and our analysis suggest that Doxycycline anhydrous poses Low risk for infant while breastfeeding and hence Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution itself shall be considered Low risk item for breastfeeding.
Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution Breastfeeding Analsys
Low RiskCAS Number: 564-25-0
Excreted into breast milk in quantities that would be clinically significant, however, intestinal absorption by infant's gut is hampered because of formation of chelating products by union with the milk's calcium. Tetracycline is at lesser amount excreted into breast milk and at higher proportion bound to calcium, hence, it is fewer absorbed than Doxycycline. Thus, it is a optimal alternative while breastfeeding. Long-term treatments are not recommended (over 3-4 weeks) since it may cause damage of the growth cartilage, teeth discoloration and imbalance of intestinal flora. Be aware of false negative results that may be obtained from infants with bacterial cultures when the mother is on antibiotics.
Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
CAS Number: 564-25-0
A number of reviews have stated that tetracyclines are contraindicated during breastfeeding because of possible staining of infants' dental enamel or bone deposition of tetracyclines. However, a close examination of available literature indicates that there is not likely to be harm in short-term use of doxycycline during lactation because milk levels are low and absorption by the infant is inhibited by the calcium in breastmilk. Short-term use of doxycycline is acceptable in nursing mothers. As a theoretical precaution, avoid prolonged or repeat courses during nursing. Monitor the infant for rash and for possible effects on the gastrointestinal flora, such as diarrhea or candidiasis (thrush, diaper rash).
What if I already have used Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution?
Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution is in the category of low risk, if you have already used it then its not a big deal if health and behavior of baby is good. However your health care provider shall be aware of the fact that you have used Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution so you should inform him based on your convenience.
My doctor has prescribed me Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution, what should I do?
Though Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution dose not comes in category of safe drugs rather it comes in category of low risk but if your doctor is aware that you are breastfeeding your baby and has still recommended it then its advantages must be outweighing the risks.
If I am using Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Not much monitoring required while using Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Doxy 100(tm) Doxycycline Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week