Maximum Strength Flu | Acetaminophen, Dextromethorphan Hbr, Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablet while Breastfeeding
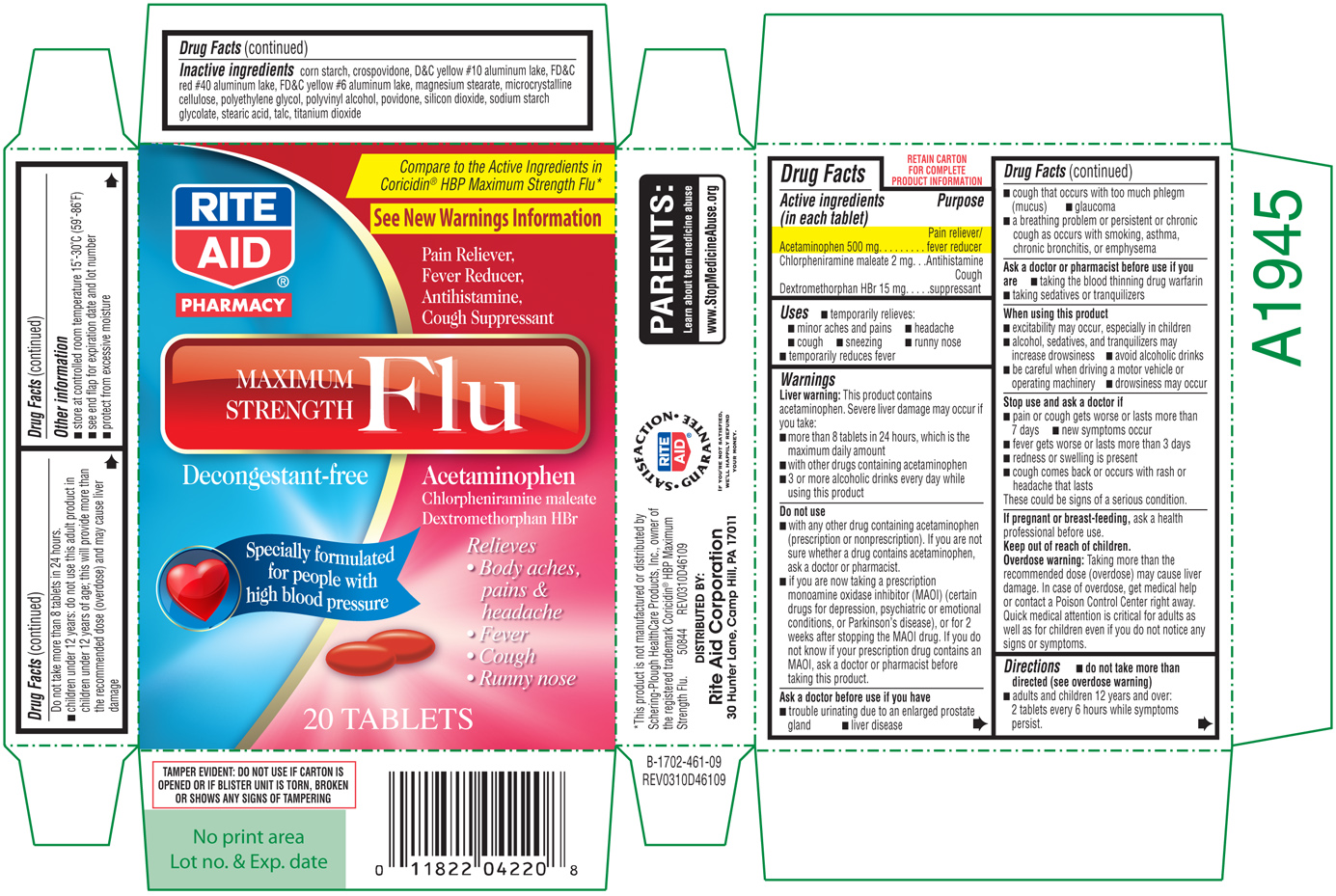
What is Maximum Strength Flu | Acetaminophen, Dextromethorphan Hbr, Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablet ?
Brief: Pain reliever/fever reducer Antihistamine Cough suppressant
Can I use Maximum Strength Flu | Acetaminophen, Dextromethorphan Hbr, Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablet while breastfeeding?

Maximum Strength Flu | Acetaminophen, Dextromethorphan Hbr, Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablet Breastfeeding Analsys
Acetaminophen while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 103-90-2
Excreted in very low amount into breast milk. Infant intake may be lower than 4% of usual pediatric dose. The American Academy of Pediatrics rates it as compatible with Breastfeeding.
Dextromethorphan hydrobromide while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 125-71-3
Cough suppressant related with morphine and codeine which is lacking of analgesic or sedative properties. Commonly prescribed by pediatricians. On latest update relevant data on breastfeeding was not found. Because reported low toxicity and mild side effect it is considered to be safe while breastfeeding. Frequently associated to caffeine and other products that are usually compatible with breastfeeding. Avoid use of multiple drug and alcohol containing medication.
Chlorpheniramine maleate while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 132-22-9
First generation antihistaminic and alchylamine drug, with sedative effect. Its active isomer is Dexchlorfeniramine. Likely inhibition of lactation within the first weeks post delivery because anti-prolactin effect.. Short-term and low dose (2 mg one or twice-day) treatment is compatible with breastfeeding. Be aware of somnolence in the child. For long-term treatment an alternative drug should be preferred. Compounds in association with expectorants, corticoids and cough relief medicines are available. Avoid drug associations especially while breastfeeding. Follow-up for sedation and feeding ability of the infant. Bed-sharing is not recommended for mothers who are taking this medication.
Maximum Strength Flu | Acetaminophen, Dextromethorphan Hbr, Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablet Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Acetaminophen while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 103-90-2
Acetaminophen is a good choice for analgesia, and fever reduction in nursing mothers. Amounts in milk are much less than doses usually given to infants. Adverse effects in breastfed infants appear to be rare.
Dextromethorphan hydrobromide while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 125-71-3
Neither the excretion of dextromethorphan in milk nor its effect on breastfed infants have been studied. It is unlikely that with usual maternal doses amounts in breastmilk would harm the nursing infant, especially in infants over 2 months of age. It is best to avoid the use of products with a high alcohol content while nursing.
Chlorpheniramine maleate while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 132-22-9
Small (2 to 4 mg), occasional doses of chlorpheniramine are acceptable during breastfeeding. Larger doses or more prolonged use might cause effects in the infant or decrease the milk supply, particularly in combination with a sympathomimetic such as spseudoephedrine or before lactation is well established. Single bedtime doses after the last feeding of the day may be adequate for many women and will minimize any effects of the drug. The nonsedating antihistamines are preferred alternatives, though.
I already used Maximum Strength Flu | Acetaminophen, Dextromethorphan Hbr, Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablet and meanwhile I breastfed my baby should I be concerned?
During whole lactation period you shall first discuss with your doctor and then together you shall decide whether you shall take that drug or not however if you have already taken Maximum Strength Flu | Acetaminophen, Dextromethorphan Hbr, Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablet then you shall inform your doctor, But you should not be worried too much as Maximum Strength Flu | Acetaminophen, Dextromethorphan Hbr, Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablet comes in category of low risk drug.
My doctor has prescribed me Maximum Strength Flu | Acetaminophen, Dextromethorphan Hbr, Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablet, what should I do?
Maximum Strength Flu | Acetaminophen, Dextromethorphan Hbr, Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablet comes in category of low risk and if your doctor is aware that you are breastfeeding it should be ok to use
If I am using Maximum Strength Flu | Acetaminophen, Dextromethorphan Hbr, Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablet, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Not much
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Maximum Strength Flu | Acetaminophen, Dextromethorphan Hbr, Chlorpheniramine Maleate Tablet in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
