Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment while Breastfeeding
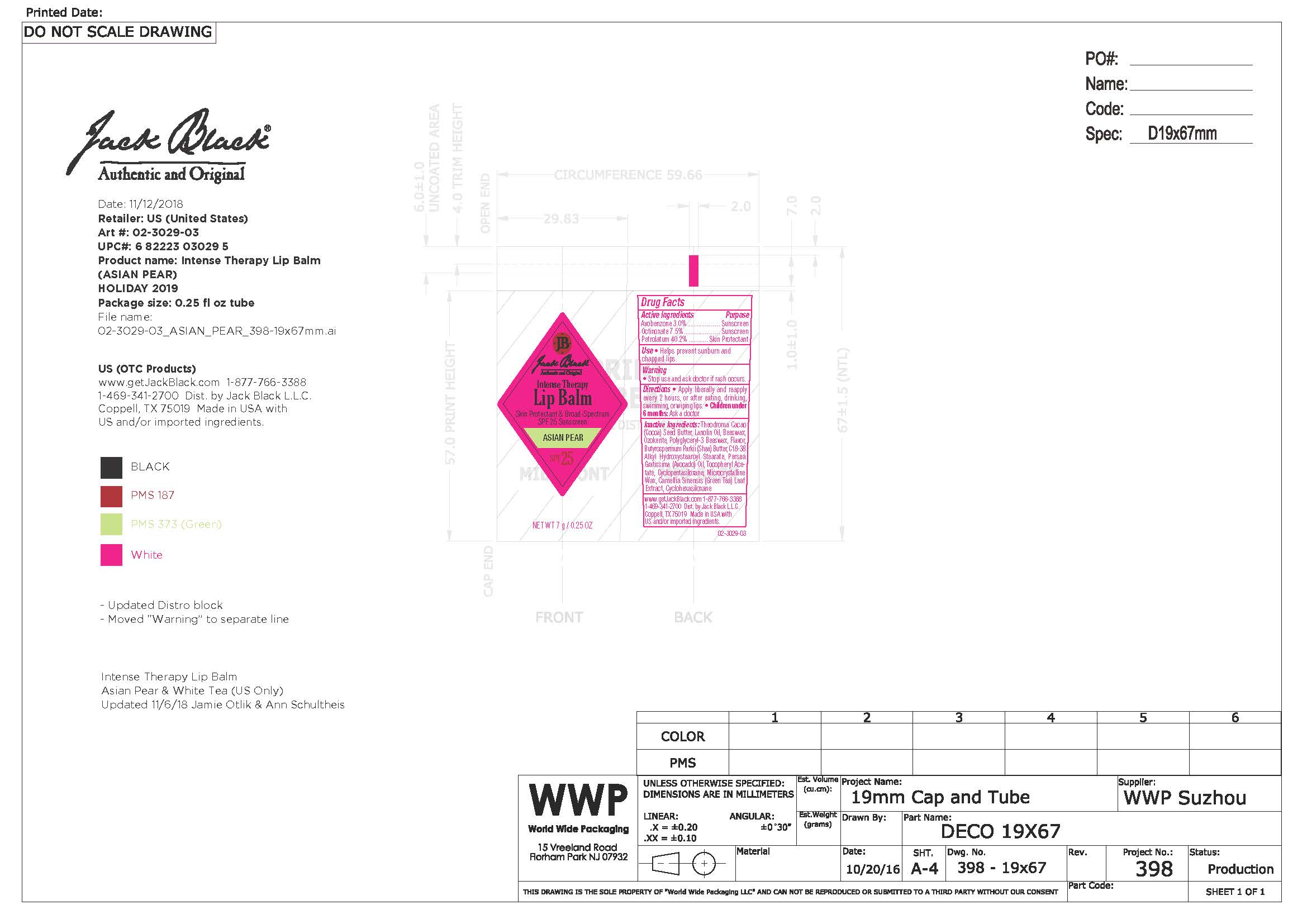
What is Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment ?
Can I use Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment while breastfeeding?

Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment Breastfeeding Analsys
Petrolatum while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 8012-95-1
Mineral oil, paraffin or petroleum jelly is a saturated hydrocarbon derived from petroleum. The length of molecular chain may range from 15 to 40 carbons with a molecular weight between 200 and 600 daltons.It is used as a laxative, also in cosmetics, as emollient and as excipient in topical products for the skin. LAXATIVE: Mineral oils with more than 34 carbons (480 daltons) are not absorbed, or, only have minimal absorption through the intestine being this a reason for which those are that should be used on humans (Hagemann 1998). Infant daily intake should be nil or less than 4 mg / kg. For oils with less than 25 carbons daily intake should not exceed 0.2 mg / kg.When used as a laxative it has been suggested, (Mahadevan 2006), although weakly evidence based, that it may interfere with the absorption of liposoluble vitamins (Gattuso 1994).Infants whose mothers received this treatment did not suffer any change on their usual bowel movements (Baldwin 1963). COSMETICS as lotions and creams (body, hands or breast) and lipsticks are a source to accumulation of saturated hydrocarbons in body fat tissue (Concin 2011). Paraffin-containing breast creams significantly increase paraffin concentration in breastmilk (Noti 2003, Concin 2008) which is a reason to be avoided as they may increase the infant's daily intake to 40 mg / kg (Noti 2003). During breastfeeding it should be wise to avoid the use of paraffin-containing creams and/or having them restricted to a minimum, not to apply them on the breast or only at least as possible when they are part of the excipient of an important topical treatment provided residual traces are been thoroughly removed before the next feeding at the breast. The use of mineral oil as a laxative should be replaced by other less risky product. Local injection of paraffin for allegedly aesthetic purposes (breast augmentation or others) is a common practice in Eastern and Southeastern Asia, has often serious complications (Alagaratnam 1996, Zekri 1996, Ho 2001, Markopoulos 2006) which is a practice pending of eradication (Di Benedetto 2002). Although published data on it is lacking, it is presumed that paraffin concentrations in breastmilk would be greatly increased in these cases.
Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Avobenzone and Breastfeeding
SafeNot much study has been done on effects of topical usage of Avobenzone during breast feeding however it is known to penetrate the skin in very limited quantity. Its not very likely to have adverse effects in breastfed infants.
Note: Study and data for tropical use only, Breakdown product causes relatively high rates of skin allergy hence stabilization is required.Warning: Tropical usage in breast area shall be avoided to prevent the Avobenzone passing orally in Infants.
Octinoxate and Breastfeeding
UnsafeOctinoxate (Octylmethoxycinnamate) has been detected in human urine, blood and breast milk and is known for moderate risk of skin allergy. Some studies suggest that Octinoxate has estrogen like effects however less than 1% skin penetration has been found in human laboratory studies. As not much study has been done on effects of Octinoxate during breast feeding its recommended to use safe alternatives.
Octyl Methoxycinnamate (OMC) is a frequently used UV-filter in sunscreens and other cosmetics. Octinoxate can be systemically absorbed after skin application, being found in the deeper layers of the stratum corneum as well as urine, plasma, and breast milk. The mean maximum plasma concentration detected after application of 2mg/cm2 sunscreen was 7ng/mL in women and 16ng/mL in men. FDA study found blood levels 13 times above cutoff for systemic exposure.
Several studies indicated that OMC acts as an endocrine disruptor due to the ability to interfere with endocrine system at different levels. In humans OMC exposure has minor, but statistically significant effects on the levels of testosterone and estradiol. Moreover, some studies suggested that OMC can interact with the hypothalamo-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis.
Moreover, a study of offspring of dams treated with OMC (500�1000 mg/kg/day) showed sex-dependent behavioral changes, namely decreased motor activity in females, but not in males, and improved spatial learning in males, suggesting that OMC can affect neuronal development, however the doses used in these experiments were extremely high, not relevant to possible human exposure.
Note: Study and data for tropical use onlyWarning: High dosage shall be avoided as reproductive system, thyroid and behavioral alterations in animal studies has been found, Tropical usage in breast area shall be avoided to prevent the OCTINOXATE passing orally in Infants.
What should I do if already breastfed my kid after using Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment?
If you observer abnormal behavior or any other health issue in infant then you should immediately call 911 or contact other contact other emergency service provider in your area otherwise closely monitor the baby and inform your doctor about your Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment usage and time interval of breastfeeding.
My doctor has prescribed me Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment, what should I do?
If your doctor knows that you are breastfeeding mother and still prescribes Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment then there must be good reason for that as Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment is considered unsafe, It usually happens when doctor finds that overall advantage of taking
If I am using Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Yes, Extra monitoring is required if mother is using Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment and breastfeeding as it is considered unsafe for baby.
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Intense Therapy Lip Balm Asian Pear | Sunscreen Skin Protectant Lip Balm Ointment in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
