Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream while Breastfeeding
What is Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream used for?
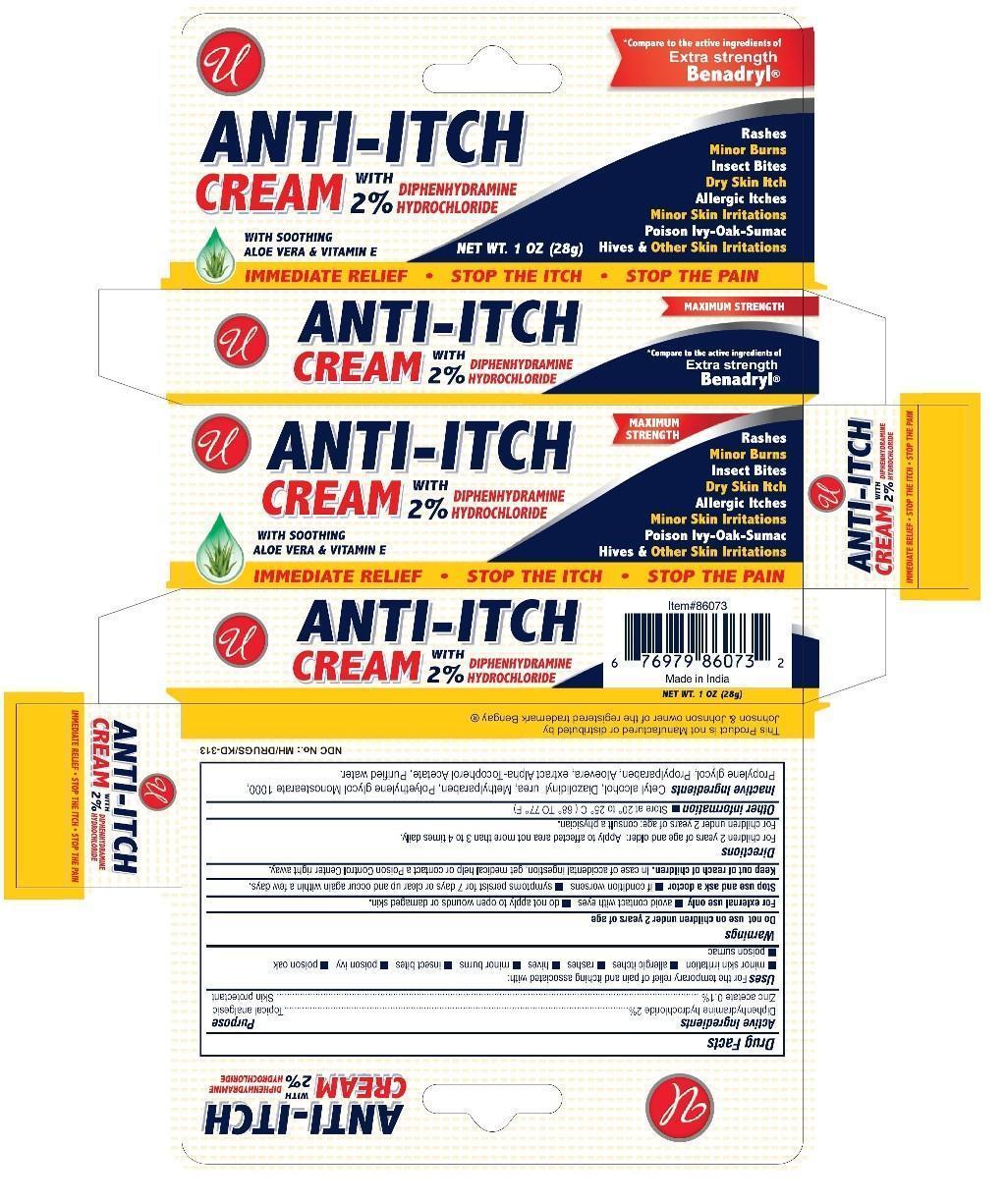
Brief: Topical Analgesic Skin Protectant
Can I continue breastfeeding if I am using Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream? How long does it stays in breast milk?

Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream Breastfeeding Analsys
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 58-73-1
It is a first generation antihistamine drug (Ethanolamine) with a strong sedative effect. A high protein-binding capacity makes difficult an excretion into breast milk in significant amounts in accordance with old studies that had confirmed it. The absorption from ingested mother's milk to the infant's plasma is hampered by a low oral bioavailability. For both, the mother and the infant is safer the use of antihistamine medication with higher safety levels without sedative effect, especially when the child is a premature or younger than 1 month old. Neither a decrease of milk production nor alteration of Prolactin release have been shown with the use of this drug. When used while breastfeeding do it with the lower dose as possible and avoid a long-term use. Check up for feeding difficulty and somnolence in the infant. Bed-sharing with the infant is not recommended for parents who are on this medication.
Zinc cation while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 557-34-6
Zinc (Zn) is an essential element for nutrition. It is present in many foods.Recommended daily allowance of Zn is 8 to 15 mg. (Moran Hall 2010). Millions of people worldwide are Zn-deficient.It is used as a treatment for Wilson's disease and Acrodermatitis Enteropathica. Zn is involved in the regulation process of lactation (Lee 2016).Pasteurization of the milk does not affect the concentration of Zn and other trace elements (Mohd Taufek-2016). The average concentration of Zn in breastmilk is 4 to 16 mg / L (Picciano 1976, Hannan 2005, Dórea 2012) which is independent of plasma levels and maternal daily intake (Krebs 1995, Chierici 1999, Hannan 2009).Intestinal absorption of zinc is almost doubled during pregnancy and lactation (Fung 1997).Zinc levels in the infant are dependent on Zinc levels in the breast milk (Dumrongwongsiri 2015)With a varied and balanced diet, an extra intake of minerals is not needed. Excessive intake of Zinc may cause gastrointestinal problems and Pancytopenia (Irving 2003).
Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 58-73-1
Small, occasional doses of diphenhydramine would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. Larger doses or more prolonged use may cause effects in the infant or decrease the milk supply, particularly in combination with a sympathomimetic such as pseudoephedrine or before lactation is well established. Single bedtime doses after the last feeding of the day may be adequate for many women and will minimize any effects of the drug. The nonsedating antihistamines are preferred alternatives.
What should I do if I am breastfeeding mother and I am already exposed to Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream?
Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream is in the category of low risk, if you have already used it then its not a big deal if health and behavior of baby is good. However your health care provider shall be aware of the fact that you have used Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream so you should inform him based on your convenience.
My doctor has prescribed me Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream, what should I do?
Though Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream dose not comes in category of safe drugs rather it comes in category of low risk but if your doctor is aware that you are breastfeeding your baby and has still recommended it then its advantages must be outweighing the risks.
If I am using Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Not much monitoring required while using Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Anti-itch | Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride And Zinc Acetate Cream in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
