Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension while Breastfeeding
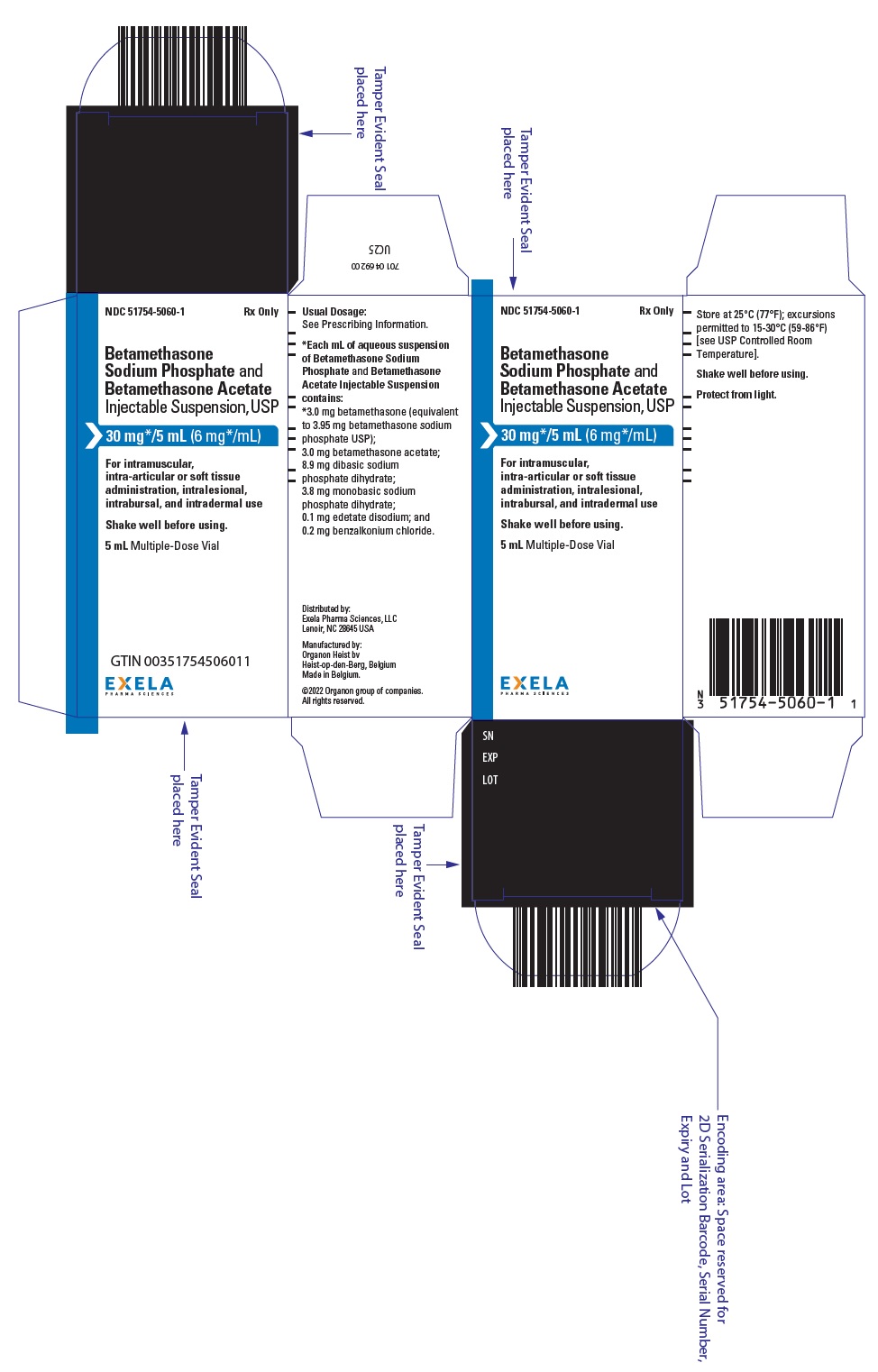
What is Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension ?
Is using Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension safe or dangerous while breastfeeding?

Nursing Mothers Systemically administered corticosteroids appear in human milk and could suppress growth, interfere with endogenous corticosteroid production, or cause other untoward effects. Caution should be exercised when corticosteroids are administered to a nursing woman.
Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension Breastfeeding Analsys
Betamethasone while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 378-44-9
Because pharmacokinetic data suggest excretion into breast milk in significant levels long lasting treatments should use other steroidal drugs known to be excreted in low amounts. When administered before delivery it may induce delay in phase II of Lactogenesis (coming-in) and a decrease of milk production within the first week post-partum. Large intra-articular doses may transitory decrease milk production. WHO Model List of Essential Drugs 2002: Compatible with breastfeeding.
Betamethasone acetate while Breastfeeding
Low RiskCAS Number: 378-44-9
Because pharmacokinetic data suggest excretion into breast milk in significant levels long lasting treatments should use other steroidal drugs known to be excreted in low amounts. When administered before delivery it may induce delay in phase II of Lactogenesis (coming-in) and a decrease of milk production within the first week post-partum. Large intra-articular doses may transitory decrease milk production. WHO Model List of Essential Drugs 2002: Compatible with breastfeeding.
Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Betamethasone while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 378-44-9
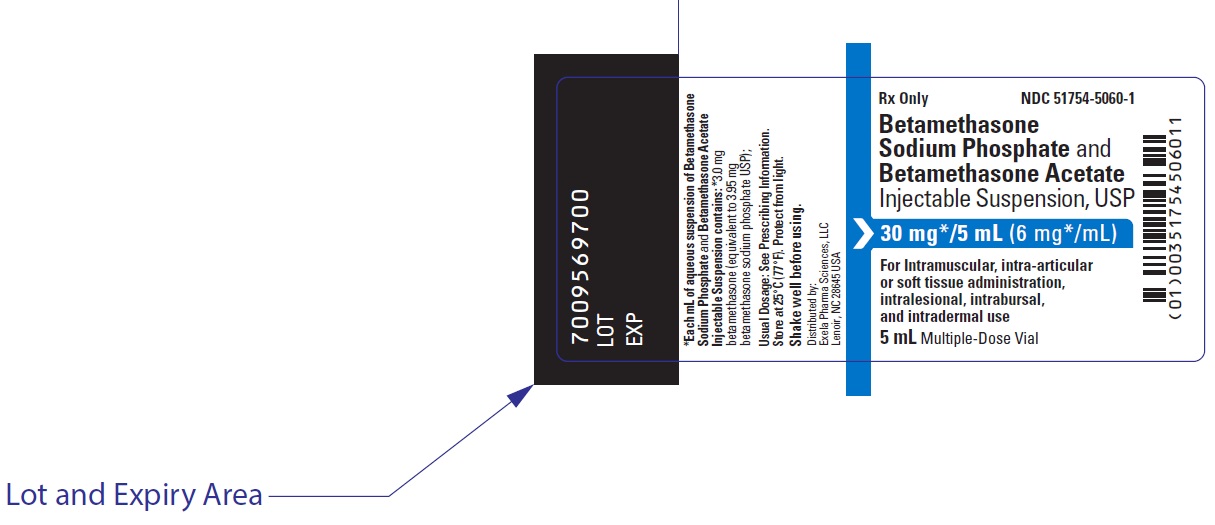
Betamethasone has not been well studied during breastfeeding after systemic or topical use. Systemic betamethasone is best avoided in favor of one of the shorter-acting and better studied alternatives because of its potency and low protein binding which would favor its passage into milk. Use of betamethasone 3 to 9 days prior to delivery of a preterm infant might decrease postpartum milk production in some women. Local injections, such as for tendinitis, would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants,[1] but might occasionally cause temporary loss of milk supply.
Betamethasone acetate while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 378-44-9
Betamethasone ointment appears to have no advantage over lanolin for treating sore nipples during breastfeeding.[1] Since only extensive application of the most potent corticosteroids may cause systemic effects in the mother, it is unlikely that short-term application of topical corticosteroids would pose a risk to the breastfed infant by passage into breastmilk. However, it would be prudent to use the least potent drug on the smallest area of skin possible. It is particularly important to ensure that the infant's skin does not come into direct contact with the areas of skin that have been treated. Only the lower potency corticosteroids should be used on the nipple or areola where the infant could directly ingest the drugs from the skin; topical betamethasone should be avoided on the nipple.[2] Only water-miscible cream or gel products should be applied to the breast because ointments may expose the infant to high levels of mineral paraffins via licking.[3] Any topical corticosteroid should be wiped off thoroughly prior to nursing if it is being applied to the breast or nipple area.
What should I do if I am breastfeeding mother and I am already exposed to Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension?
Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension is in the category of low risk, if you have already used it then its not a big deal if health and behavior of baby is good. However your health care provider shall be aware of the fact that you have used Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension so you should inform him based on your convenience.
My doctor has prescribed me Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension, what should I do?
Though Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension dose not comes in category of safe drugs rather it comes in category of low risk but if your doctor is aware that you are breastfeeding your baby and has still recommended it then its advantages must be outweighing the risks.
If I am using Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension, will my baby need extra monitoring?
Not much monitoring required while using Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate And Betamethasone Acetate Injection, Suspension in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
