Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered while Breastfeeding
What is Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered ?
Can I use Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered while breastfeeding?

Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered Breastfeeding Analsys
Sodium picosulfate while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 10040-45-6
Stimulant of the intestine and laxative drug through irritation of mucosa which is similar to bisacodyl. Its low oral bioavailability with minimal intestinal absorption causes plasma levels to be very low, that explains the observed failure of excretion into breast milk (undetectable levels).Authorized for use in infants from age one month old. To prevent or treat constipation is essential to have a balanced and fiber-rich diet, with a lot of fluids and exercise.
Magnesium oxide while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 1309-48-4
Ingested Magnesium does not concentrate into breast milk. Naturally occurring, the mean Magnesium concentration in the milk is 31 mg/L (range 15 – 64 mg/L) and not affected by the ingestion of Magnesium. Because of a low oral bioavailability the pass from the breast milk toward the infant's plasma is hampered, except in premature and newborn infants who may exhibit a higher intestinal absorption due to an increased permeability. Avoid chronic or excessive use. WHO Model List of Essential Medicines 2002: Magnesium oxide is compatible with breastfeeding.
Anhydrous citric acid while Breastfeeding
SafeCAS Number: 77-92-9
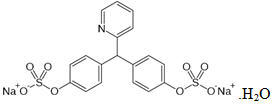
Product that is naturally found in most fruits, especially citrus ones, and which is industrially produced through fermentation of sugar by the fungus Aspergillus niger. It is used in medical compounds as effervescent, to treat intestinal affections, as antioxidant, as an agent for alkalizing urine and dissolution of urinary tract stones. In the food industry it is used as additive (E 330) due to its antioxidant, preservative and flavoring properties. Devoid of toxicity when used at appropriate doses.
Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered Breastfeeding Analsys - 2
Sodium picosulfate while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 10040-45-6
Sodium picosulfate is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and its active metabolite, which is absorbed, is not detectable in breastmilk. Sodium picosulfate can be taken during breastfeeding and no special precautions are required.
Magnesium oxide while Breastfeeding
CAS Number: 1309-48-4
No information is available on the clinical use of magnesium oxide during breastfeeding. However, other magnesium salts have been studied. A study on the use of magnesium hydroxide during breastfeeding found no adverse reactions in breastfed infants. Intravenous magnesium increases milk magnesium concentrations only slightly. Oral absorption of magnesium by the infant is poor, so maternal magnesium hydroxide is not expected to affect the breastfed infant's serum magnesium. Magnesium oxide supplementation during pregnancy might delay the onset of lactation, but it can be taken during breastfeeding and no special precautions are required.
What should I do if already breastfed my kid after using Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered?
Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered is safe in breastfeeding and should not create any health problem for your baby but in case you feel any health issue associated with Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered you should contact your doctor or health care provider. Be it pregnancy or lactation you shall keep your doctor informed.
My doctor has prescribed me Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered, what should I do?
Definitely, Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered is safe in lactation for baby. No wonder your doctor has recommended it.
If I am using Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered, will my baby need extra monitoring?
No extra baby monitoring required while mother is using Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered
Who can I talk to if I have questions about usage of Prepopik | Sodium Picosulfate, Magnesium Oxide, And Anhydrous Citric Acid Powder, Metered in breastfeeding?
US
National Womens Health and Breastfeeding Helpline: 800-994-9662 (TDD 888-220-5446) 9 a.m. and 6 p.m. ET, Monday through Friday
UK
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 0300-100-0212 9.30am to 9.30pm, daily
Association of Breastfeeding Mothers: 0300-330-5453
La Leche League: 0345-120-2918
The Breastfeeding Network supporter line in Bengali and Sylheti: 0300-456-2421
National Childbirth Trust (NCT): 0300-330-0700
Australia
National Breastfeeding Helpline: 1800-686-268 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
Canada
Telehealth Ontario for breastfeeding: 1-866-797-0000 24 hours a day, 7 days a week
